Suppression of Fibrinolysis and Hypercoagulability, Severity of Hypoxemia, and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35412597
- PMCID: PMC9250792
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004239
Suppression of Fibrinolysis and Hypercoagulability, Severity of Hypoxemia, and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 causes hypercoagulability, but the association between coagulopathy and hypoxemia in critically ill patients has not been thoroughly explored. This study hypothesized that severity of coagulopathy would be associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome severity, major thrombotic events, and mortality in patients requiring intensive care unit-level care.
Methods: Viscoelastic testing by rotational thromboelastometry and coagulation factor biomarker analyses were performed in this prospective observational cohort study of critically ill COVID-19 patients from April 2020 to October 2020. Statistical analyses were performed to identify significant coagulopathic biomarkers such as fibrinolysis-inhibiting plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and their associations with clinical outcomes such as mortality, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation requirement, occurrence of major thrombotic events, and severity of hypoxemia (arterial partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen categorized into mild, moderate, and severe per the Berlin criteria).
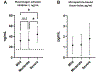
Results: In total, 53 of 55 (96%) of the cohort required mechanical ventilation and 9 of 55 (16%) required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation-naïve patients demonstrated lysis indices at 30 min indicative of fibrinolytic suppression on rotational thromboelastometry. Survivors demonstrated fewer procoagulate acute phase reactants, such as microparticle-bound tissue factor levels (odds ratio, 0.14 [0.02, 0.99]; P = 0.049). Those who did not experience significant bleeding events had smaller changes in ADAMTS13 levels compared to those who did (odds ratio, 0.05 [0, 0.7]; P = 0.026). Elevations in plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (odds ratio, 1.95 [1.21, 3.14]; P = 0.006), d-dimer (odds ratio, 3.52 [0.99, 12.48]; P = 0.05), and factor VIII (no clot, 1.15 ± 0.28 vs. clot, 1.42 ± 0.31; P = 0.003) were also demonstrated in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation-naïve patients who experienced major thrombotic events. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 levels were significantly elevated during periods of severe compared to mild and moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome (severe, 44.2 ± 14.9 ng/ml vs. mild, 31.8 ± 14.7 ng/ml and moderate, 33.1 ± 15.9 ng/ml; P = 0.029 and 0.039, respectively).
Conclusions: Increased inflammatory and procoagulant markers such as plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, microparticle-bound tissue factor, and von Willebrand factor levels are associated with severe hypoxemia and major thrombotic events, implicating fibrinolytic suppression in the microcirculatory system and subsequent micro- and macrovascular thrombosis in severe COVID-19.
Copyright © 2022, the American Society of Anesthesiologists. All Rights Reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Hypoxia and Hypercoagulability in COVID-19: Chicken or the Egg?Anesthesiology. 2022 Jul 1;137(1):13-14. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004241. Anesthesiology. 2022. PMID: 35522846 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Esper SA, Levy JH, Waters JH, Welsby IJ. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the adult: a review of anticoagulation monitoring and transfusion. Anesth Analg 2014. Apr;118(4):731–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

