Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Common Among ART-Treated People With HIV
- PMID: 35413022
- PMCID: PMC9246928
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003000
Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Is Common Among ART-Treated People With HIV
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available regarding asymptomatic COVID-19 among people with HIV (PWH). Data on a representative subset of PWH enrolled in Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV, a global clinical trial, are presented here.
Methods: Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV is an atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention trial among 7770 PWH on antiretroviral therapy. Beginning April 2020, targeted data on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diagnosis and symptoms were collected during routine trial visits. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection was defined as either COVID-19 clinical diagnosis or presence of SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin G (IgG) or Immunoglobulin A (IgA) receptor binding domain protein (antispike) antibodies in the absence of prior COVID-19 vaccine.
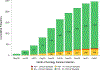
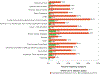
Results: The group (N = 2464) had a median age 53 years, 35% female sex, 47% Black or African American race, median CD4 count 649 c/mm 3 , and 97% with HIV VL <400 cp/m. SARS-CoV-2 infection occurred in 318 persons (13%): 58 with clinical diagnosis and 260 with detectable antibodies. Of these PWH, 304 completed symptom questionnaires: 121 (40%) reported symptoms, but 183 (60%) were asymptomatic. PWH with asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection were more likely to be from low-income or middle-income regions, of Black or African American race, older in age, and with higher atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score. Symptomatic COVID was more common with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and low HDL levels. CD4 counts and HIV viral suppression rates were similar among PWH with symptomatic vs. asymptomatic COVID.
Conclusions: Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection is common among antiretroviral therapy-treated PWH globally. We determined that 60% of infections in PWH were asymptomatic. HIV clinicians must remain vigilant about COVID-19 testing among PWH to identify asymptomatic cases.
Copyright © 2022 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Geretti AM, Stockdale AJ, Kelly SH, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 related hospitalization among people with HIV in the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol (UK): a prospective observational study. Clin Infect Dis 2020. Oct 23:ciaa1605. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1605. Online ahead of print. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK040561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL123339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069452/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA047045/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

