Autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients with chronic kidney disease: a safe and effective option
- PMID: 35413986
- PMCID: PMC9200631
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-022-01657-y
Autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients with chronic kidney disease: a safe and effective option
Abstract
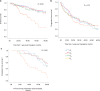
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a frequent complication in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and is associated with adverse outcomes. The use of autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) has improved disease outcomes, however, the safety and efficacy of ASCT in patients with CKD has been the subject of debate. To investigate this, we conducted a retrospective analysis of 370 MM patients who underwent their first ASCT, including those with mild, moderate and severe CKD as well as normal renal function at the time of transplant. No significant difference in ASCT-related mortality, Progression-Free or Overall Survival was noted between the different renal function groups. A decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) at 1-year of >8.79% was associated with poorer overall survival (p < 0.001). The results of this study show that ASCT is a safe and effective option for myeloma patients with CKD, including those on dialysis. Patients who demonstrate renal deterioration at 1-year post-transplant should be closely monitored as this is a predictor for poor survival.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Augustson B. Earlymortality after diagnosis of multiple myeloma: analysis of patients entered ontothe United kingdom Medical Research Council trials between 1980 and 2002—Medical Research Council Adult Leukaemia Working Party. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9219–26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.2086. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

