Cutaneous Invasive Fungal Infections with Saksenaea Species in Immunocompetent Patients in Europe: A Systematic Review and Case Report
- PMID: 35415064
- PMCID: PMC8994077
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004230
Cutaneous Invasive Fungal Infections with Saksenaea Species in Immunocompetent Patients in Europe: A Systematic Review and Case Report
Abstract
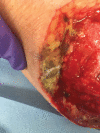
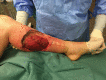
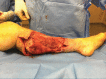
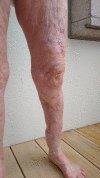
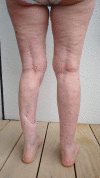
Invasive fungal infections from Saksenaea, a fungus belonging to the Mucorales, have been rarely reported in central European climate zones. This study aims to raise awareness of invasive cutaneous infections with Saksenaea species. The first case of a cutaneous infection was diagnosed in Switzerland in an immunocompetent 79-year-old patient. A minor skin trauma of her left lower leg led to a fulminant infection causing necrosis and extensive loss of tissue. The combination of surgical debridement and administration of antifungal agents averted a prolonged course with a possible worse outcome. A pedicled hemisoleus muscle flap was used to reconstruct the defect and treatment was continued for 63 days.
Methods: A systematic review in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic review and Meta-Analysis guidelines was conducted to identify all European cases of infection with Saksenaea species in immunocompetent hosts. The epidemiology, clinical presentation, microbiological diagnosis, and management of cases reported in Europe were summarized and analyzed.
Conclusions: The prognosis of soft tissue infections with Saksenaea species. depends on early diagnosis and appropriate antifungal and surgical treatment. Reconstruction can be successful under ongoing antifungal treatment.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures


References
-
- Bartram L, Aaron JG. Fungal necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2019;13:146–156.
-
- Prabhu RM, Patel R. Mucormycosis and entomophthoramycosis: a review of the clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004;10 suppl 1:31–47. - PubMed
-
- Jeong W, Keighley C, Wolfe R, et al. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25:26–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
