Plasma p217+tau versus NAV4694 amyloid and MK6240 tau PET across the Alzheimer's continuum
- PMID: 35415202
- PMCID: PMC8984092
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.12307
Plasma p217+tau versus NAV4694 amyloid and MK6240 tau PET across the Alzheimer's continuum
Abstract
Introduction: We evaluated a new Simoa plasma assay for phosphorylated tau (P-tau) at aa217 enhanced by additional p-tau sites (p217+tau).
Methods: Plasma p217+tau levels were compared to 18F-NAV4694 amyloid beta (Aβ) positron emission tomography (PET) and 18F-MK6240 tau PET in 174 cognitively impaired (CI) and 223 cognitively unimpaired (CU) participants.
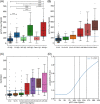
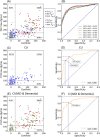
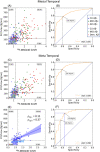
Results: Compared to Aβ- CU, the plasma levels of p217+tau increased 2-fold in Aβ+ CU and 3.5-fold in Aβ+ CI. In Aβ- the p217+tau levels did not differ significantly between CU and CI. P217+tau correlated with Aβ centiloids P = .67 (CI, P = .64; CU, P = .45) and tau SUVRMT P = .63 (CI, P = .69; CU, P = .34). Area under curve (AUC) for Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia versus Aβ- CU was 0.94, for AD dementia versus other dementia was 0.93, for Aβ+ versus Aβ- PET was 0.89, and for tau+ versus tau- PET was 0.89.
Discussion: Plasma p217+tau levels elevate early in the AD continuum and correlate well with Aβ and tau PET.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Aβ imaging; amyloid imaging; amyloid plaque; blood biomarkers; blood diagnostic for Alzheimer's disease; paired helical filaments; phosphorylated tau; plasma P‐tau217; positron emission tomography; tau imaging.
© 2022 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Christopher C. Rowe has received research grants from NHMRC, Enigma Australia, Biogen, Eisai, and Abbvie. He is on the scientific advisory board for Cerveau Technologies and consulted for Prothena, Eisai, Roche, and Biogen Australia. Victor Villemagne is and has been a consultant or paid speaker at sponsored conference sessions for Eli Lilly, Life Molecular Imaging, GE Healthcare, Abbvie, Lundbeck, Shanghai Green Valley Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, and Hoffmann La Roche. Ashley Bush is a shareholder in Alterity Ltd, Cogstate Ltd, and Mesoblast Ltd. He is a paid consultant for, and has a profit share interest in, Collaborative Medicinal Development Pty Ltd. He has received lecture fees from Biogen and Merck Sharp & Dohme P/L. Ziad Saad, Gallen Triana‐Baltzer, Randy Slemmon, and Hartmuth Kolb are employees of Janssen R&D. The other authors did not report any conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sevigny J, Suhy J, Chiao P, et al. Amyloid PET screening for enrichment of early‐stage Alzheimer disease clinical trials: experience in a phase 1b clinical trial. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2016;30:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura A, Kaneko N, Villemagne VL, et al. High performance plasma amyloid‐beta biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2018;554:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Karikari TK, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:422–433. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
