3D-printed NIR-responsive shape memory polyurethane/magnesium scaffolds with tight-contact for robust bone regeneration
- PMID: 35415289
- PMCID: PMC8965852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.12.032
3D-printed NIR-responsive shape memory polyurethane/magnesium scaffolds with tight-contact for robust bone regeneration
Abstract
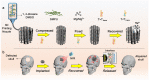
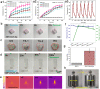
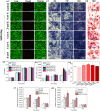
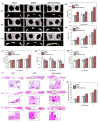
Patients with bone defects suffer from a high rate of disability and deformity. Poor contact of grafts with defective bones and insufficient osteogenic activities lead to increased loose risks and unsatisfied repair efficacy. Although self-expanding scaffolds were developed to enhance bone integration, the limitations on the high transition temperature and the unsatisfied bioactivity hindered greatly their clinical application. Herein, we report a near-infrared-responsive and tight-contacting scaffold that comprises of shape memory polyurethane (SMPU) as the thermal-responsive matrix and magnesium (Mg) as the photothermal and bioactive component, which fabricated by the low temperature rapid prototyping (LT-RP) 3D printing technology. As designed, due to synergistic effects of the components and the fabrication approach, the composite scaffold possesses a homogeneously porous structure, significantly improved mechanical properties and stable photothermal effects. The programmed scaffold can be heated to recover under near infrared irradiation in 60s. With 4 wt% Mg, the scaffold has the balanced shape fixity ratio of 93.6% and shape recovery ratio of 95.4%. The compressed composite scaffold could lift a 100 g weight under NIR light, which was more than 1700 times of its own weight. The results of the push-out tests and the finite element analysis (FEA) confirmed the tight-contacting ability of the SMPU/4 wt%Mg scaffold, which had a signficant enhancement compared to the scaffold without shape memory effects. Furthermore, The osteopromotive function of the scaffold has been demonstrated through a series of in vitro and in vivo studies. We envision this scaffold can be a clinically effective strategy for robust bone regeneration.
Keywords: 3D printing; Magnesium; Robust bone regeneration; Shape memory polyurethane; Tight-contact.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures



References
-
- Collins M.N., Ren G., Young K., Pina S., Reis R.L., Oliveira J.M. Scaffold fabrication technologies and structure/function properties in bone tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020:2010609. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202010609. n/a(n/a) - DOI
-
- Koons G.L., Diba M., Mikos A.G. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020;5(8):584–603. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-0204-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

