Polio by the Numbers-A Global Perspective
- PMID: 35415741
- PMCID: PMC9556648
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiac130
Polio by the Numbers-A Global Perspective
Abstract
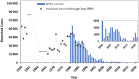
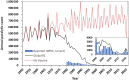
Background: Investments in national immunization programs and the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) have resulted in substantial reductions in paralytic polio worldwide. However, cases prevented because of investments in immunization programs and GPEI remain incompletely characterized.
Methods: Using a global model that integrates polio transmission, immunity, and vaccine dynamics, we provide estimates of polio incidence and numbers of paralytic cases prevented. We compare the results with reported cases and estimates historically published by the World Health Organization.
Results: We estimate that the existence and use of polio vaccines prevented 5 million cases of paralytic polio for 1960-1987 and 24 million cases worldwide for 1988-2021 compared to a counterfactual world with no polio vaccines. Since the 1988 resolution to eradicate polio, our estimates suggest GPEI prevented 2.5-6 million cases of paralytic polio compared to counterfactual worlds without GPEI that assume different levels of intensity of polio vaccine use in routine immunization programs.
Conclusions: Analysis of historical cases provides important context for understanding and communicating the benefits of investments made in polio eradication. Prospective studies will need to explore the expected benefits of future investments, the outcomes of which will depend on whether and when polio is globally eradicated.
Keywords: disease eradication; modeling; polio; prevention; vaccines.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures



Comment in
-
Economics of Eradication: Counting on the Polio Experience.J Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 17;226(8):1301-1303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac132. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35417552 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thompson KM, Duintjer Tebbens RJ. Retrospective cost-effectiveness analyses for polio vaccination in the United States. Risk Anal 2006; 26:1423–40. - PubMed
-
- Pan American Health Organization . The Americas conquer polio!https://iris.paho.org/bitstream/handle/10665.2/33556/sne1604.pdf. Accessed 1 January 2022.
-
- Duintjer Tebbens RJ, Pallansch MA, Cochi SL, et al. . Economic analysis of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative. Vaccine 2010; 29:334–43. - PubMed
-
- Global Polio Eradication Initiative . Financing.https://polioeradication.org/financing/. Accessed 3 January 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

