COVID-19 severity from Omicron and Delta SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 35415869
- PMCID: PMC9111734
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12982
COVID-19 severity from Omicron and Delta SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
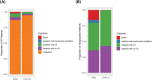
The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 achieved worldwide dominance in late 2021. Early work suggests that infections caused by the Omicron variant may be less severe than those caused by the Delta variant. We sought to compare clinical outcomes of infections caused by these two strains, confirmed by whole genome sequencing, over a short period of time, from respiratory samples collected from SARS-CoV-2 positive patients at a large medical center. We found that infections caused by the Omicron variant caused significantly less morbidity, including admission to the hospital and requirement for oxygen supplementation, and significantly less mortality than those caused by the Delta variant.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delta; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; severity; whole genome sequencing (WGS).
© 2022 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest to share.
Figures
References
-
- Cele S, Jackson L, Khoury DS, et al. SARS‐CoV‐2 Omicron has extensive but incomplete escape of Pfizer BNT162b2 elicited neutralization and requires ACE2 for infection. medRxiv. 2021.
-
- WHO . Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS‐CoV‐2 variant of concern. 2022.
-
- CDC . CDC COVID Data Tracker. Accessed February 24, 2022. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

