In rheumatoid arthritis patients, total IgA1 and IgA2 levels are elevated: implications for the mucosal origin hypothesis
- PMID: 35416963
- PMCID: PMC9788813
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac237
In rheumatoid arthritis patients, total IgA1 and IgA2 levels are elevated: implications for the mucosal origin hypothesis
Abstract
Objective: Mucosal initiated immune responses may be involved in the pathophysiology of RA. The most abundant immunoglobulin at mucosal surfaces is IgA, of which two subclasses exist: IgA1 and IgA2. IgA2 is mainly present at mucosal sites and has been ascribed pro-inflammatory properties. As IgA subclasses might provide insights into mucosal involvement and pro-inflammatory mechanisms, we investigated IgA responses in sera of RA patients.
Methods: In two cohorts of RA patients, the EAC and IMPROVED, total IgA1 and IgA2 were measured by ELISA. Furthermore, IgA subclass levels of RF and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (anti-CCP2) were determined. The association of these IgA subclass levels with CRP and smoking was investigated.
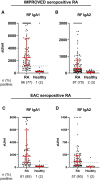
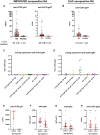
Results: Total IgA1 and IgA2 were increased in RA patients compared with healthy donors in both cohorts. This increase was more pronounced in seropositive RA vs seronegative RA. For RF and anti-CCP2, both IgA1 and IgA2 could be detected. No strong associations were found between IgA subclasses (total, RF and anti-CCP2) and CRP. In smoking RA patients, a trend towards a selective increase in total IgA2 and RF IgA1 and IgA2 was observed.
Conclusion: RA patients have raised IgA1 and IgA2 levels. No shift towards IgA2 was observed, indicating that the increase in total IgA is not due to translocation of mucosal IgA into the bloodstream. However, mucosal inflammation might play a role, given the association between smoking and total IgA2 levels. Despite its pro-inflammatory properties, IgA2 does not associate strongly with pro-inflammatory markers in RA patients.
Keywords: ACPA; IgA subclasses; RA; mucosal immunity; rheumatoid factor.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Presence of salivary IgA anti-citrullinated protein antibodies associate with higher disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Nov 23;22(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02363-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33225988 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of IgA rheumatoid factor subclasses.Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Jul;54(7):578-81. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.7.578. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995. PMID: 7668901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical significance of IgA rheumatoid factor subclasses in rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;24(11):2119-22. J Rheumatol. 1997. PMID: 9375869
-
Subclass distribution and size of human IgA rheumatoid factor at mucosal and nonmucosal sites.Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):831-9. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340708. Arthritis Rheum. 1991. PMID: 2059231
-
Immunoglobulin A Antibodies: From Protection to Harmful Roles.Immunol Rev. 2024 Nov;328(1):171-191. doi: 10.1111/imr.13424. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39578936 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Autoantibodies against citrullinated and native proteins and prediction of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A nested case-control study.Lancet Rheumatol. 2023 Feb;5(2):e77-e87. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(22)00380-0. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36874209 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of IgA anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and rheumatoid factor in an early arthritis population with a treat-to-target approach.Immunol Res. 2024 Oct;72(5):982-990. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09500-w. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38960995 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of Fab-dependent IgA antibody recognition by gut-bacterial metallopeptidases.EMBO J. 2025 Sep;44(17):4867-4898. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00518-w. Epub 2025 Jul 31. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40745064 Free PMC article.
-
B-Cell Receptor Repertoire: Recent Advances in Autoimmune Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Feb;66(1):76-98. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08984-6. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38459209 Review.
-
Antibodies against citrullinated proteins of IgA isotype are associated with progression to rheumatoid arthritis in individuals at-risk.RMD Open. 2023 Jan;9(1):e002705. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002705. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 36717186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Svard A, Kastbom A, Sommarin Y, Skogh T.. Salivary IgA antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunobiology 2013;218:232–7. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Zhang D, Jia H. et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat Med 2015;21:895–905. - PubMed
-
- Woof JM, Russell MW.. Structure and function relationships in IgA. Mucosal Immunol 2011;4:590–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

