Synaptic vesicle binding of α-synuclein is modulated by β- and γ-synucleins
- PMID: 35417693
- PMCID: PMC9116446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110675
Synaptic vesicle binding of α-synuclein is modulated by β- and γ-synucleins
Erratum in
-
Synaptic vesicle binding of α-synuclein is modulated by β- and γ-synucleins.Cell Rep. 2024 May 28;43(5):114280. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114280. Epub 2024 May 16. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38758645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
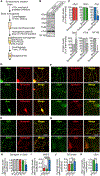
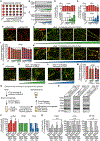
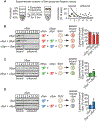
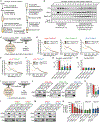
α-synuclein, β-synuclein, and γ-synuclein are abundantly expressed proteins in the vertebrate nervous system. α-synuclein functions in neurotransmitter release by binding to and clustering synaptic vesicles and chaperoning SNARE-complex assembly. Pathologically, aggregates originating from soluble pools of α-synuclein are deposited into Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies. The functions of β-synuclein and γ-synuclein in presynaptic terminals remain poorly studied. Using in vitro liposome binding studies, circular dichroism spectroscopy, immunoprecipitation, and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) experiments on isolated synaptic vesicles in combination with subcellular fractionation of brains from synuclein mouse models, we show that β-synuclein and γ-synuclein have a reduced affinity toward synaptic vesicles compared with α-synuclein, and that heteromerization of β-synuclein or γ-synuclein with α-synuclein results in reduced synaptic vesicle binding of α-synuclein in a concentration-dependent manner. Our data suggest that β-synuclein and γ-synuclein are modulators of synaptic vesicle binding of α-synuclein and thereby reduce α-synuclein's physiological activity at the neuronal synapse.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; Parkinson’s disease; interaction; membrane binding; multimers; neurodegeneration; synapse; synaptic vesicle; synuclein; synucleinopathy.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, et al. (2000). Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25, 239–252. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M, Attoub S, Singh MN, Martin FL, and El-Agnaf OM (2007). Gamma-synuclein and the progression of cancer. FASEB J. 21, 3419–3430. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JP, Walker DE, Goldstein JM, de Laat R, Banducci K, Caccavello RJ, Barbour R, Huang J, Kling K, Lee M, et al. (2006). Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 29739–29752. - PubMed
-
- Arawaka S, Saito Y, Murayama S, and Mori H (1998). Lewy body in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1 is immunoreactive for alpha-synuclein. Neurology 51, 887–889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

