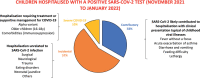
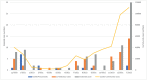
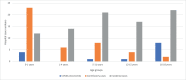
Very low rates of severe COVID-19 in children hospitalised with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in London, England"
- PMID: 35417737
- PMCID: PMC9645775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.04.020
Very low rates of severe COVID-19 in children hospitalised with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in London, England"
Abstract
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pediatric patients with immune-mediated diseases on immunosuppressants have low risk of severe COVID-19 and no increase in flare rate after SARS CoV-2 exposure.J Infect. 2022 Sep;85(3):e62-e65. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.06.012. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 35724754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Immunocompromised children and young people are at no increased risk of severe COVID-19.J Infect. 2022 Jan;84(1):31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 14. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 34785268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castagnoli R., Votto M., Licari A., et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in children and adolescents: a systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2020;174(9):882–889. - PubMed
-
- UK Health Security Agency. Official Statistics: National flu and COVID-19 surveillance reports: 2021 to 2022 season. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/national-flu-and-covid-19-surve... (accessed 05 February 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

