Development and Validation of an Analytical Method to Quantitate Hydroxycitric Acid, the Key Constituent in Garcinia cambogia Extract, in Rodent Plasma and Fetus
- PMID: 35418711
- PMCID: PMC9004611
- DOI: 10.1080/00032719.2021.2005618
Development and Validation of an Analytical Method to Quantitate Hydroxycitric Acid, the Key Constituent in Garcinia cambogia Extract, in Rodent Plasma and Fetus
Abstract
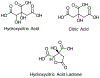
Garcinia cambogia extract (GCE) is a popular botanical supplement used in weight loss products. Hydroxycitric acid (HCA) is the principal component in GCE. Due to lack of adequate toxicity data to assess the safe use of GCE, the National Toxicology Program is testing GCE in Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD® rats following perinatal exposure and in adult B6C3F1/N mice. We report a validated method utilizing sample clean up with ultrafiltration followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis to quantify HCA in rat plasma over the concentration range of 20 to 800 ng/mL. The method was linear (r2 ≥ 0.99) with the limits of quantitation (LOQ) and detection (LOD) of 20.0 and 3.9 ng/mL plasma, respectively. The accuracy (determined as relative error, RE) and precision (determined as relative standard deviation, RSD) using Quality Control standards analyzed over multiple days were ≤ ± 7.5% and ≤ 9.5%, respectively. The method can be applied to quantify HCA in study matrices (RE ≤ ± 23.0%; RSD ≤ 6.0) except gestational day (GD)18 fetus. The method was partially validated in GD18 fetal homogenate over the concentration range 60-3000 ng/g (r2 ≥ 0.99, RE ≤ ± 11.9%, and RSD ≤ 5.5%; LOQ 60.0 ng/g; LOD 7.77 ng/g). The standards as high as 20,000 ng/mL (plasma) and 502,000 ng/g (fetus) can successfully be quantified after diluting into the validated range (RE ≤ ± 2.6%; RSD ≤ 5.2%). These data demonstrate that the method is suitable to quantify HCA in rodent matrices and can be adapted to other biological matrices.
Keywords: Garcinia cambogia extract; botanical dietary supplements; hydroxycitric acid; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS); ultrafiltration clean-up; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bakhiya N, Ziegenhagen R, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Dusemund B, Richter K, Schultrich K, Pevny S, Schäfer B, and Lampen A. 2017. Phytochemical compounds in sport nutrition: Synephrine and hydroxycitric acid (HCA) as examples for evaluation of possible health risks. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research. 61(6): 1601020. - PubMed
-
- Bhutani P, Rekha U, Shivakumar HN, Ranjanna PK, and Paul AT. 2020. Rapid and cost-effective LC–MS/MS method for determination of hydroxycitric acid in plasma: Application in the determination of pharmacokinetics in commercial Garcinia preparations. Biomedical Chromatography. 34(10): e4902. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BI, Zito G, Colquhoun R, Martinez N, Kendall K, Buchanan L, Lehn M, Johnson M, St C. Louis Y. Smith, Cloer B, and Pingel A. 2016. The effects of a single-dose thermogenic supplement on resting metabolic rate and hemodynamic variables in healthy females--a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Journal of International Society of Sports Nutrition. 13:14. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Carvalho Cruz A, Suenaga EM, Prova SS, de Oliveira Neto JR, Ifa DR, and da Cunha LC. 2020. New bioanalytical method for the quantification of (−) - hydroxycitric acid in human plasma using UPLC-MS/MS and its application in a Garcinia cambogia pharmacokinetic study. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 188:113385. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
