The impact of different volumetric thresholds to determine progressive disease in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab
- PMID: 35419519
- PMCID: PMC9000300
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac032
The impact of different volumetric thresholds to determine progressive disease in patients with recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab
Abstract
Background: The optimal volumetric threshold for determining progressive disease (PD) in recurrent glioblastoma is yet to be determined. We investigated a range of thresholds in association with overall survival (OS).
Methods: First recurrent glioblastoma patients treated with bevacizumab and/or lomustine were included from the phase II BELOB and phase III EORTC26101 trials. Enhancing and nonenhancing tumor volumes were measured at baseline, first (6 weeks), and second (12 weeks) follow-up. Hazard ratios (HRs) for the appearance of new lesions and several thresholds for tumor volume increase were calculated using cox regression analysis. Results were corrected in a multivariate analysis for well-established prognostic factors.
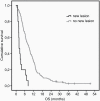
Results: At first and second follow-up, 138 and 94 patients respectively, were deemed eligible for analysis of enhancing volumes, while 89 patients were included in the analysis of nonenhancing volumes at first follow-up. New lesions were associated with a significantly worse OS (3.2 versus 11.2 months, HR = 7.03, P < .001). At first follow-up a threshold of enhancing volume increase of ≥20% provided the highest HR (5.55, p = .001. At second follow-up, any increase in enhancing volume (≥0%) provided the highest HR (9.00, p < .001). When measuring nonenhancing volume at first follow-up, only 6 additional patients were scored as PD with the highest HR of ≥25% increase in volume (HR=3.25, p = .008).
Conclusion: Early appearing new lesions were associated with poor OS. Lowering the volumetric threshold for PD at both first and second follow-up improved survival prediction. However, the additional number of patients categorized as PD by lowering the threshold was very low. The per-RANO added change in nonenhancing volumes to the analyses was of limited value.
Keywords: GBM; RANO; bevacizumab; volumetry.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. . Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomized phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MH, Shen YL, Keegan P, Pazdur R. FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Oncologist 2009;14(11):1131–1138. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, et al. . Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(11):1963–1972. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, ScholdSC, Jr, Cairncross JG. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8(7):1277–1280. - PubMed
-
- Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981;47(1):207–214. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
