Clinical Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Adults with ESKD Receiving Outpatient Hemodialysis
- PMID: 35419540
- PMCID: PMC8986054
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0004372021
Clinical Course of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Adults with ESKD Receiving Outpatient Hemodialysis
Abstract
Background: Patients with ESKD on maintenance dialysis receive dialysis in common spaces with other patients and have a higher risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infections. They may have persistently or intermittently positive SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR tests after infection. We describe the clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the serologic response in a convenience sample of patients with ESKD to understand the duration of infectivity.
Methods: From August to November 2020, we enrolled patients on maintenance dialysis with SARS-CoV-2 infections from outpatient dialysis facilities in Atlanta, Georgia. We followed participants for approximately 42 days. We assessed COVID-19 symptoms and collected specimens. Oropharyngeal (OP), anterior nasal (AN), and saliva (SA) specimens were tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, using RT-PCR, and sent for viral culture. Serology, including neutralizing antibodies, was measured in blood specimens.
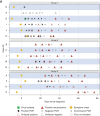
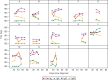
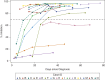
Results: Fifteen participants, with a median age of 58 (range, 37‒77) years, were enrolled. Median duration of RT-PCR positivity from diagnosis was 18 days (interquartile range [IQR], 8‒24 days). Ten participants had at least one, for a total of 41, positive RT-PCR specimens ≥10 days after symptoms onset. Of these 41 specimens, 21 underwent viral culture; one (5%) was positive 14 days after symptom onset. Thirteen participants developed SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies, 11 of which included neutralizing antibodies. RT-PCRs remained positive after seroconversion in eight participants and after detection of neutralizing antibodies in four participants; however, all of these samples were culture negative.
Conclusions: Patients with ESKD on maintenance dialysis remained persistently and intermittently SARS-CoV-2-RT-PCR positive. However, of the 15 participants, only one had infectious virus, on day 14 after symptom onset. Most participants mounted an antibody response, including neutralizing antibodies. Participants continued having RT-PCR-positive results in the presence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies, but without replication-competent virus detected.
Keywords: COVID-19; ESRD; SARS-CoV-2; chronic kidney failure; dialysis; end-stage renal disease; infectiousness; infectivity; outpatients.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
I. Apata reports having consultancy agreements with the CDC. L. S. Dalrymple reports having ownership interest in Fresenius Medical Care (via share options) and owning stock in GE; serving as a member of the Kidney Care Quality Alliance Steering Committee, cochair of the Kidney Health Initiative (KHI) ESRD Global Data Standard Workgroup, and cochair of the National Quality Forum Renal Standing Committee; and serving on the Kidney Medicine editorial board. L. S. Dalrymple also reports her husband owned stock in Bayer, CVS, and GE in the last 36 months, and has shares in The Permanente Medical Group. P. R. Patel reports having other interests in/relationships with American Association of Kidney Patients. R. L. Wingard reports having ownership interest in Fresenius Medical Care North America (via stock options), serving as a member of the KHI Muscle Cramping PRO Project, and serving as a volunteer for Welcome Home of Chattanooga (a nonprofit). All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J, Rajagopalan H, O’Donnell L, Chernyak Y, Tobin KA, Cerfolio RJ, Francois F, Horwitz LI: Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 369: m1966, 2020. 10.1136/bmj.m1966 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flythe JE, Assimon MM, Tugman MJ, Chang EH, Gupta S, Shah J, Sosa MA, Renaghan AD, Melamed ML, Wilson FP, Neyra JA, Rashidi A, Boyle SM, Anand S, Christov M, Thomas LF, Edmonston D, Leaf DE; STOP-COVID Investigators : Characteristics and outcomes of individuals with pre-existing kidney disease and COVID-19 admitted to intensive care units in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 77: 190–203.e1, 2021. 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention : People with certain medical conditions, 2020. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-.... Accessed March 29, 2021
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

