Current State of MRI-Guided Endovascular Arterial Interventions: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies
- PMID: 35420239
- PMCID: PMC9790618
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.28205
Current State of MRI-Guided Endovascular Arterial Interventions: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Abstract
Background: MRI guidance of arterial endovascular interventions could be beneficial as it does not require radiation exposure, allows intrinsic blood-tissue contrast, and enables three-dimensional and functional imaging, however, clinical applications are still limited.
Purpose: To review the current state of MRI-guided arterial endovascular interventions and to identify the most commonly reported challenges.
Study type: Systematic review.
Population: Pubmed, Embase, Web of Science, and The Cochrane Library were systematically searched to find relevant articles. The search strategy combined synonyms for vascular pathology, endovascular therapy, and real-time MRI guidance.
Field strength/sequence: No field strength or sequence restrictions were applied.
Assessment: Two reviewers independently identified and reviewed the original articles and extracted relevant data.
Statistical tests: Results of the included original articles are reported.
Results: A total of 24,809 studies were identified for screening. Eighty-eight studies were assessed for eligibility, after which data were extracted from 43 articles (6 phantom, 33 animal, and 4 human studies). Reported technical success rates for animal and human studies ranged between 42% to 100%, and the average complication rate was 5.8% (animal studies) and 8.8% (human studies). Main identified challenges were related to spatial and temporal resolution as well as safety, design, and scarcity of current MRI-compatible endovascular devices.
Data conclusion: MRI guidance of endovascular arterial interventions seems feasible, however, included articles included mostly small single-center case series. Several hurdles remain to be overcome before larger trials can be undertaken. Main areas of research should focus on adequate imaging protocols with integrated tracking of dedicated endovascular devices.
Keywords: MRI-guided endovascular arterial interventions; clinical outcomes; current challenges.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
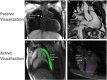
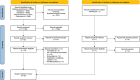
References
-
- Bakker C, Hoogeveen R, Hurtak W, Van Vaals J, Viergever M, Mali W. MR‐guided endovascular interventions: Susceptibility‐based catheter and near‐real‐time imaging technique. Radiology 1997;202(1):273‐276. - PubMed
-
- Dumoulin CL, Souza SP, Darrow RD. Real‐time position monitoring of invasive devices using magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 1993;29(3):411‐415. - PubMed
-
- Clogenson HC, Van Den Dobbelsteen JJ. Catheters and guidewires for interventional MRI: Are we there yet? J Imaging Interv Radiol 2016;2(2):28‐32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

