Trends of Cancer Screenings, Diagnoses, and Mortalities During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications and Future Recommendations
- PMID: 35420510
- PMCID: PMC9014329
- DOI: 10.1177/00031348221091948
Trends of Cancer Screenings, Diagnoses, and Mortalities During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications and Future Recommendations
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern.Am Surg. 2025 Mar;91(3):464-472. doi: 10.1177/00031348241305412. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Am Surg. 2025. PMID: 39791244 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer screenings and care has yet to be determined. This study aims to investigate the screening, diagnosis, and mortality rates of the top five leading causes of cancer mortality in the United States from 2019 to 2021 to determine the potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer care.
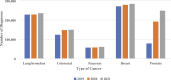
Methods: A retrospective cohort study investigating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on screening, diagnoses, and mortality rates of the top five leading causes of cancer death (lung/bronchus, colon/rectum, pancreas, breast, and prostate), as determined by the National Institute of Health (NIH) utilizing The United States Healthcare Cost Institute and American Cancer Society databases from 2019 to 2021.
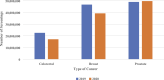
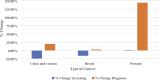
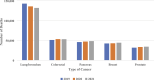
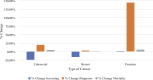
Results: Screenings decreased by 24.98% for colorectal cancer and 16.01% for breast cancer from 2019 to 2020. Compared to 2019, there was a .29% increase in lung/bronchus, 19.72% increase in colorectal, 1.46% increase in pancreatic, 2.89% increase in breast, and 144.50% increase in prostate cancer diagnoses in 2020 (all P < .01). There was an increase in the total number of deaths from colorectal, pancreatic, breast, and prostate cancers from 2019 to 2021.
Conclusion: There was a decrease in the screening rates for breast and colorectal cancer, along with an increase in the estimated incidence and mortality rate among the five leading causes of cancer deaths from 2019 to 2021. The findings suggest that the COVID-19 pandemic is associated with impaired cancer screening, diagnosis, and care, and further emphasizes the need for proactive screening and follow-up to prevent subsequent cancer morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: cancer diagnosis; cancer mortalities; cancer screening; covid-19 pandemic; prevention interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Martin K, Kurowski D, Given P, Kennedy K, Clayton E. The Impact of COVID-19 on the Use of Preventive Health Care. 2021. Accessed January 6, 2022. https://healthcostinstitute.org/hcci-research/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-....
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer facts and statistics. 2022. Accessed January 23, 2022. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics.html
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

