Integrated use of phosphorus, farmyard manure and biofertilizer improves the yield and phosphorus uptake of black gram in silt loam soil
- PMID: 35421141
- PMCID: PMC9009712
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266753
Integrated use of phosphorus, farmyard manure and biofertilizer improves the yield and phosphorus uptake of black gram in silt loam soil
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Integrated use of phosphorus, farmyard manure and biofertilizer improves the yield and phosphorus uptake of black gram in silt loam soil.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 31;17(8):e0273465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273465. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36044404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
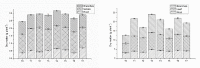
An experiment on the use of farmyard manure and biofertilizer along with application of chemical phosphorus was conducted to assess the impact of differential doses of phosphorus, farmyard manure and consortium biofertilizer application on the development, yield and phosphorus uptake during the year 2018 and 2019. The impact of different treatments was recorded on the plant height, dry matter partition, yield and yield attributes, phosphorus uptake and soil phosphorus availability using standard methods. The data revealed significant improvement in yield, yield attributes, phosphorus uptake and soil phosphorus availability. The integration of farmyard manure and biofertilizer with 60 kg ha-1 SSP (single superphosphate) has improved the black gram yield by 7.4% and 3.28% respectively over the use of 60 SSP alone. The phosphorus uptake in black gram with application of Farm yard manure and biofertilizer along with 60 kg ha-1 SSP has improved the uptake by 7.18% and 2.51% respectively over the use of 60 kg ha-1 SSP alone. The results highlight the need of integrated application of farm yard manure, biofertilizer for sustainable production of black gram in the region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Gour YD, Microbiology, physiology and agronomy of nitrogen fixation: Legume-Rhizobium symbiosis. Proc. Indian Nat Sci Acad, 1993;59:333–358.
-
- Anonymous 2018, Agricultural statistics at a glance 2018. Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Department of Agriculture and Cooperation, Govt. of India; 2018 New Delhi.
-
- Bargaz A, Faghire M, Abdi N, Farissi M, Sifi B, Drevon JJ, et al.. Low soil phosphorus availability increases acid phosphatases activities and affects P partitioning in nodules, Seeds and Rhizosphere of Phaseolus vulgaris. Agriculture 2012; 2:139–153. doi: 10.3390/agriculture2020139 - DOI
-
- Sepetoglu H, Grain legumes. Department of Field Crops, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Ege, Yzmir, Turkey. 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

