Rapid and efficient degradation of endogenous proteins in vivo identifies stage-specific roles of RNA Pol II pausing in mammalian development
- PMID: 35421370
- PMCID: PMC9047393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.03.013
Rapid and efficient degradation of endogenous proteins in vivo identifies stage-specific roles of RNA Pol II pausing in mammalian development
Abstract
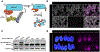
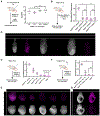
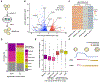
Targeted protein degradation methods offer a unique avenue to assess a protein's function in a variety of model systems. Recently, these approaches have been applied to mammalian cell culture models, enabling unprecedented temporal control of protein function. However, the efficacy of these systems at the tissue and organismal levels in vivo is not well established. Here, we tested the functionality of the degradation tag (dTAG) degron system in mammalian development. We generated a homozygous knock-in mouse with a FKBP12F36V tag fused to negative elongation factor b (Nelfb) locus, a ubiquitously expressed regulator of transcription. In our validation of targeted endogenous protein degradation across mammalian development and adulthood, we demonstrate that irrespective of the route of administration the dTAG system is non-toxic, rapid, and efficient in embryos from the zygote-to-mid-gestation stages. Additionally, acute depletion of NELFB revealed a specific role in zygote-to-2-cell development and zygotic genome activation (ZGA).
Keywords: NELF; ZGA; dTAG; degron; mouse embryo; pausing; post-implantation; pre-implantation; transcription; zygote.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.-K.H. is on the advisory board for Developmental Cell. All other authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- TL1 TR002386/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD086478/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH085726/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS092096/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD094868/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012051/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD035455/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007739/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HD103398/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

