Identification of key lipid metabolites during metabolic dysregulation in the diabetic retinopathy disease mouse model and efficacy of Keluoxin capsule using an UHPLC-MS-based non-targeted lipidomics approach
- PMID: 35423075
- PMCID: PMC8694764
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra00343c
Identification of key lipid metabolites during metabolic dysregulation in the diabetic retinopathy disease mouse model and efficacy of Keluoxin capsule using an UHPLC-MS-based non-targeted lipidomics approach
Abstract
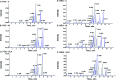
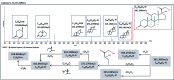
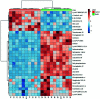
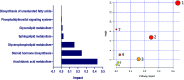
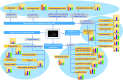
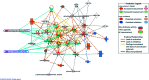
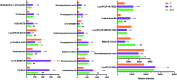
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is an important complication of diabetes, and is currently the main cause of blindness among young adults in the world. Previous studies have shown that Keluoxin (KLX) capsules have a significant effect on DR in C57BL/KsJ/db-/- mice (db/db mice), however the unclear mechanism limits its further clinical application and actual value. Further research is urgently needed for the treatment of DR disease. Discovery of key lipid biomarkers and metabolic pathways can reveal and explore the molecular mechanisms related to DR development and discover the effect of Keluoxin (KLX) capsule against DR in db/db mice. Lipidomics has been used for characterizing the pathological conditions via identification of key lipid metabolites and the metabolic pathway. In this study, the high-throughput lipidomics using UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS combined with multivariate statistical analysis, querying multiple network databases and employing ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) method for molecular target prediction. A total of 30 lipid biomarkers were identified and 7 metabolic pathways including arachidonic acid metabolism and steroid hormone biosynthesis were found. The preventive effect of KLX intervention can regulate 22 biomarkers such as LysoPA(16:0/0:0), prostaglandin D2, cortisol and γ-linolenic acid, etc. IPA platform has predicted that PI3K/MAPK pathway are closely related to DR development. It also showed that high-throughput lipidomics combined with multivariate statistical analysis could deep excavate of the biological significance of the big data, and can provide molecular targets information about the disease treatment.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

