Impact of Intraoperative Molecular Imaging after Fluorescent-Guided Pulmonary Metastasectomy for Sarcoma
- PMID: 35426386
- PMCID: PMC9460458
- DOI: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000132
Impact of Intraoperative Molecular Imaging after Fluorescent-Guided Pulmonary Metastasectomy for Sarcoma
Abstract
Background: Intraoperative molecular imaging (IMI) has been shown to improve lesion detection during pulmonary sarcomatous metastasectomy. Our goal in this study was to evaluate whether data garnered from IMI-guided resection of pulmonary sarcoma metastasis translate to improved patient outcomes.
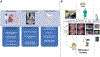
Study design: Fifty-two of 65 consecutive patients with a previous history of sarcomas found to have pulmonary nodules during screening were enrolled in a nonrandomized clinical trial. Patients underwent TumorGlow the day before surgery. Data on patient demographics, tumor biologic characteristics, preoperative assessment, and survival were included in the study analysis and compared with institutional historical data of patients who underwent metastasectomy without IMI. p values < 0.05 were considered significant.
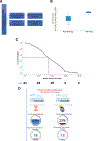
Results: IMI detected 42 additional lesions in 31 patients (59%) compared with the non-IMI cohort where 25% percent of patients had additional lesions detected using tactile and visual feedback only (p < 0.05). Median progression-free survival (PFS) for patients with IMI-guided pulmonary sarcoma metastasectomy was 36 months vs 28.6 months in the historical cohort (p < 0.05). IMI-guided pulmonary sarcoma metastasectomy had recurrence in the lung with a median time of 18 months compared with non-IMI group at 13 months (p < 0.05). Patients with synchronous lesions in the IMI group underwent systemic therapy at a statistically higher rate and tended to undergo routine screening at shorter interval.
Conclusions: IMI identifies a subset of sarcoma patients during pulmonary metastasectomy who have aggressive disease and informs the medical oncologist to pursue more aggressive systemic therapy. In this setting, IMI can serve both as a diagnostic and prognostic tool without conferring additional risk to the patient.
Copyright © 2022 by the American College of Surgeons. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


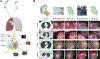

Comment in
-
Invited Commentary: Intraoperative Molecular Imaging Not Only Facilitates Detection of Pulmonary Metastases but Also Improves Survival.J Am Coll Surg. 2022 May 1;234(5):759. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000139. J Am Coll Surg. 2022. PMID: 35426387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marcove RC, Miké V, Hajek JV, et al. Osteogenic sarcoma under the age of twenty-one. A review of one hundred and forty-five operative cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970;52:411–423. - PubMed
-
- Saltzman DA, Snyder CL, Ferrell KL, et al. Aggressive metastasectomy for pulmonic sarcomatous metastases: A follow-up study. Am J Surg 1993;166:543–547. - PubMed
-
- Predina JD, Puc MM, Bergey MR, et al. Improved survival after pulmonary metastasectomy for soft tissue sarcoma. J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:913–919. - PubMed
-
- Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS, McCarty TP, et al. A prospective study to determine the incidence of non-imaged malignant pulmonary nodules in patients who undergo metastasectomy by thoracotomy with lung palpation. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1696–700; discussion 1700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

