A Highly Potent SARS-CoV-2 Blocking Lectin Protein
- PMID: 35426678
- PMCID: PMC9017247
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00006
A Highly Potent SARS-CoV-2 Blocking Lectin Protein
Abstract
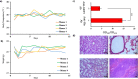
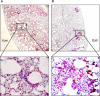
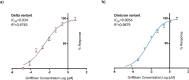
The COVID-19 (coronavirus disease-19) pandemic affected more than 180 million people around the globe, causing more than five million deaths as of January 2022. SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), the new coronavirus, has been identified as the primary cause of the infection. The number of vaccinated people is increasing; however, prophylactic drugs are highly demanded to ensure secure social contact. A number of drug molecules have been repurposed to fight against SARS-CoV-2, and some of them have been proven to be effective in preventing hospitalization or ICU admissions. Here, we demonstrated griffithsin (GRFT), a lectin protein, to block the entry of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, Delta and Omicron, into the Vero E6 cell lines and IFNAR-/- mouse models by attaching to the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Given the current mutation frequency of SARS-CoV-2, we believe that GRFT protein-based drugs will have a high impact in preventing the transmission of both the Wuhan strain as well as any other emerging variants, including Delta and Omicron variants, causing the high-speed spread of COVID-19.
Keywords: Please add keywords.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gorbalenya A. E.; Baker S. C.; Baric R. S.; de Groot R. J.; Drosten C.; Gulyaeva A. A.; Haagmans B. L.; Lauber C.; Leontovich A. M.; Neuman B. W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Wu F.; Zhao S.; Yu B.; Chen Y. M.; Wang W.; Song Z. G.; Hu Y.; Tao Z. W.; Tian J. H.; Pei Y. Y.; Yuan M. L.; Zhang Y. L.; Dai F. H.; Liu Y.; Wang Q. M.; Zheng J. J.; Xu L.; Holmes E. C.; Zhang Y. Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zhou P.; Yang X. L.; Wang X. G.; Hu B.; Zhang L.; Zhang W.; Si H. R.; Zhu Y.; Li B.; Huang C. L.; Chen H. D.; Chen J.; Luo Y.; Guo H.; Jiang R. D.; Liu M. Q.; Chen Y.; Shen X. R.; Wang X.; Zheng X. S.; Zhao K.; Chen Q. J.; Deng F.; Liu L. L.; Yan B.; Zhan F. X.; Wang Y. Y.; Xiao G. F.; Shi Z. L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Ghebreyesus T.WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19-2020. 2020.
-
- Chan J. F. W.; Kok K. H.; Zhu Z.; Chu H.; To K. K. W.; Yuan S. F.; Yuen K. Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lan J.; Ge J. W.; Yu J. F.; Shan S. S.; Zhou H.; Fan S. L.; Zhang Q.; Shi X. L.; Wang Q. S.; Zhang L. Q.; Wang X. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. 10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5. - DOI - PubMed
- Yan R. H.; Zhang Y. Y.; Li Y. N.; Xia L.; Guo Y. Y.; Zhou Q. Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. 10.1126/science.abb2762. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

