Long-term outcomes for ibrutinib-rituximab and chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: updated results of the E1912 trial
- PMID: 35427411
- PMCID: PMC9283968
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021014960
Long-term outcomes for ibrutinib-rituximab and chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: updated results of the E1912 trial
Abstract
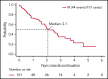
Herein, we present the long-term follow-up of the randomized E1912 trial comparing the long-term efficacy of ibrutinib-rituximab (IR) therapy to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) and describe the tolerability of continuous ibrutinib. The E1912 trial enrolled 529 treatment-naïve patients aged ≤70 years with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Patients were randomly assigned (2:1 ratio) to receive IR or 6 cycles of FCR. With a median follow-up of 5.8 years, median progression-free survival (PFS) is superior for IR (hazard ratio [HR], 0.37; P < .001). IR improved PFS relative to FCR in patients with both immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV) gene mutated CLL (HR: 0.27; P < .001) and IGHV unmutated CLL (HR: 0.27; P < .001). Among the 354 patients randomized to IR, 214 (60.5%) currently remain on ibrutinib. Among the 138 IR-treated patients who discontinued treatment, 37 (10.5% of patients who started IR) discontinued therapy due to disease progression or death, 77 (21.9% of patients who started IR) discontinued therapy for adverse events (AEs)/complications, and 24 (6.8% of patients who started IR) withdrew for other reasons. Progression was uncommon among patients able to remain on ibrutinib. The median time from ibrutinib discontinuation to disease progression or death among those who discontinued treatment for a reason other than progression was 25 months. Sustained improvement in overall survival (OS) was observed for patients in the IR arm (HR, 0.47; P = .018). In conclusion, IR therapy offers superior PFS relative to FCR in patients with IGHV mutated or unmutated CLL, as well as superior OS. Continuous ibrutinib therapy is tolerated beyond 5 years in the majority of CLL patients. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02048813.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures




Comment in
-
Ibrutinib frontline in young patients with CLL.Blood. 2022 Jul 14;140(2):80-81. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016535. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35834283 No abstract available.
References
-
- Byrd JC, O’Brien S, James DF. Ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(13):1278-1279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 CA193541/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233290/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233230/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA190140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196172/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA232760/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189863/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014236/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233180/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233253/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

