Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental and Alveolar Bone Tissues Regeneration: An Innovative Scope Review
- PMID: 35429315
- PMCID: PMC9294090
- DOI: 10.1007/s13770-022-00438-4
Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental and Alveolar Bone Tissues Regeneration: An Innovative Scope Review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Demineralized Dentin Matrix for Dental and Alveolar Bone Tissues Regeneration: An Innovative Scope Review.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022 Aug;19(4):887-889. doi: 10.1007/s13770-022-00463-3. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022. PMID: 35594009 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Dentin is a permeable tubular composite and complex structure, and in weight, it is composed of 20% organic matrix, 10% water, and 70% hydroxyapatite crystalline matrix. Demineralization of dentin with gradient concentrations of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, 0.6 N hydrochloric acid, or 2% nitric acid removes a major part of the crystalline apatite and maintains a majority of collagen type I and non-collagenous proteins, which creates an osteoinductive scaffold containing numerous matrix elements and growth factors. Therefore, demineralized dentin should be considered as an excellent naturally-derived bioactive material to enhance dental and alveolar bone tissues regeneration.
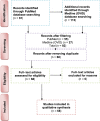
Method: The PubMed and Midline databases were searched in October 2021 for the relevant articles on treated dentin matrix (TDM)/demineralized dentin matrix (DDM) and their potential roles in tissue regeneration.
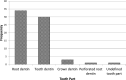
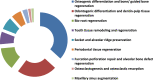
Results: Several studies with different study designs evaluating the effect of TDM/DDM on dental and bone tissues regeneration were found. TDM/DDM was obtained from human or animal sources and processed in different forms (particles, liquid extract, hydrogel, and paste) and different shapes (sheets, slices, disc-shaped, root-shaped, and barrier membranes), with variable sizes measured in micrometers or millimeters, demineralized with different protocols regarding the concentration of demineralizing agents and exposure time, and then sterilized and preserved with different techniques. In the act of biomimetic acellular material, TDM/DDM was used for the regeneration of the dentin-pulp complex through direct pulp capping technique, and it was found to possess the ability to activate the odontogenic differentiation of stem cells resident in the pulp tissues and induce reparative dentin formation. TDM/DDM was also considered for alveolar ridge and maxillary sinus floor augmentations, socket preservation, furcation perforation repair, guided bone, and bioroot regenerations as well as bone and cartilage healing.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, there are no standard procedures to adopt a specific form for a specific purpose; therefore, future studies are required to come up with a well-characterized TDM/DDM for each specific application. Likely as decellularized dermal matrix and prospectively, if the TDM/DDM is supplied in proper consistency, forms, and in different sizes with good biological properties, it can be used efficiently instead of some widely-used regenerative biomaterials.
Keywords: Bone regeneration; Demineralized dentin matrix; Dental tissue regeneration; Dentin; Treated dentin matrix.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
