Anti-blastocystosis activity of antioxidant coated ZIF-8 combined with mesoporous silicas MCM-41 and KIT-6
- PMID: 35431315
- PMCID: PMC9013716
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10397-4
Anti-blastocystosis activity of antioxidant coated ZIF-8 combined with mesoporous silicas MCM-41 and KIT-6
Abstract
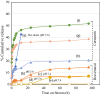
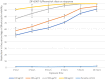
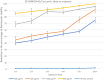
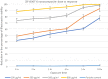
The biocompatible hybrid Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8)/structured silica nanocomposite can be loaded with antioxidants such as curcumin and resveratrol to offer multiple advantages of drug functionalization and structural stability. blastocystosis, an enteric parasite, has various outcomes and its treatment includes drugs which have side effects and do not result in a full cure. We aimed to design novel biocompatible nanocomposites containing natural antioxidant, resveratrol or curcumin and ZIF-8/mesoporous silica. We also assessed their anti-blastocystosis activities as bioactive novel nanocomposites. The nano-silica (MCM-41 and KIT-6) was synthesized using a hydrothermal technique and made composite with ZIF-8 using an ultrasonic technique. The antioxidants, curcumin and resveratrol, were loaded over ZIF-8/MCM-41 and ZIF-8/KIT-6 using a rotary evaporator technique to form novel nanocomposites with bioactive properties. The formulated nanocomposites were characterized. To test their biological activity, suspension of cultured blastocystosis cysts (subtype 3) were exposed to increasing concentrations of nanocomposites and the minimal lethal concentration of each nanocomposite was calculated. The bioactive nanocomposites (ZIF-8/KIT-6, ZIF-8/KIT-6/Resveratrol and ZIF-8/MCM-41/Curcumin) were formulated. Anti-blastocystosis activity of the tested nanocomposites was both dose and time dependent. ZIF-8/KIT-6/Resveratol showed the maximum percentage of growth inhibition (~ 100%) at a concentration of 500 µg/ml after 5 h of exposure. More than 90% of blastocystosis cysts' growth was significantly inhibited at all concentrations of ZIF-8/MCM-41/Curcumin, with different times of exposure, while it occurred only at the highest concentration of ZIF-8/KIT-6 (800 µg/ml). Using cheap, simple, reproducible and scalable techniques, we nano-formulated innovative bioactive nanocomposites, by incorporating the bioactive ZIF-8 (Zn2+ with imidazole), structured mesosilica and natural antioxidant compounds, curcumin or resveratrol, to generate multifunctional modalities. These eco-friendly, naturally based, safe, economical, biocompatible, and bioavailable nanocomposites are potential nanotherapeutics. The anti-blastocystosis results of these three nanocomposites indicate their potentially promising innovative and safe use as alternative Blastocystosis therapies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Zeolitic Imidazole Framework/Silica Nanocomposite for Targeted Cancer Therapeutics: Comparative Study of Chemo-Drug Cisplatin (CPt) and Green Platinum (GPt) Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 9;25(6):3157. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063157. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542131 Free PMC article.
-
Ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on cholesterol oxidase-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle@ZIF-8 core-shell nanocomposites for detection of cholesterol.Talanta. 2018 Oct 1;188:708-713. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.019. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Talanta. 2018. PMID: 30029436
-
ZIF-8 nanocarriers synthesized by co-encapsulating resveratrol and cellulase for biomedical applications.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;283(Pt 4):137756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137756. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39557232
-
Recent advancement of imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) based nanoformulations for synergistic tumor therapy.Nanoscale. 2019 Nov 28;11(44):21030-21045. doi: 10.1039/c9nr06558j. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Nanoscale. 2019. PMID: 31674617 Review.
-
Enemies or Allies? Hormetic and Apparent Non-Dose-Dependent Effects of Natural Bioactive Antioxidants in the Treatment of Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 4;25(3):1892. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031892. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bionanocomposites comprising mesoporous metal organic framework (ZIF-8) phytofabricated with Allium sativum as alternative nanomaterials to combat antimicrobial drug resistance.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2024 Aug;47(8):1335-1344. doi: 10.1007/s00449-024-03027-y. Epub 2024 May 20. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2024. PMID: 38767741
-
Zeolitic Imidazole Framework/Silica Nanocomposite for Targeted Cancer Therapeutics: Comparative Study of Chemo-Drug Cisplatin (CPt) and Green Platinum (GPt) Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 9;25(6):3157. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063157. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542131 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Nov 24;8(1):435. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01654-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37996406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Intervention Against Microplastic Hazards.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;14(7):797. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070797. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Moura Ferraz LR, Tabosa AÉGA, da Silva Nascimento DDS, Ferreira AS, de Albuquerque Wanderley Sales V, Silva JYR, et al. ZIF-8 as a promising drug delivery system for benznidazole: Development, characterization, in vitro dialysis release and cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020;10(1):16815. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73848-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

