Enhanced water absorption of tissue paper by cross-linking cellulose with poly(vinyl alcohol)
- PMID: 35431412
- PMCID: PMC8992785
- DOI: 10.1007/s11696-022-02188-y
Enhanced water absorption of tissue paper by cross-linking cellulose with poly(vinyl alcohol)
Abstract
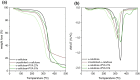
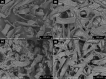
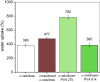
Abstract: Tissue paper was the only paper grade whose consumption increased during 2020 in Europe. In a highly competitive context, this work explores a strategy based on bisacrylamide cross-linkers and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), seeking to enhance the water uptake of pulps for tissue paper and the key properties of the resulting tissue sheets: water absorption capacity, capillarity, softness, porosity, and strength. For that, α-cellulose from cotton and a kraft hardwood pulp, in parallel, were reacted with N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide, both in the absence and in the presence of PVA. The water desorption rate of the modified polymers was monitored. Pulp blends were then mixed with a conventional softwood pulp (30%) to prepare laboratory tissue paper sheets (20 g m-2). For cotton cellulose, cross-linking with PVA more than doubled the water uptake, up to 7.3 g/g. A significant enhancement was also obtained in the case of pulps, up to 9.6 g/g, and in the case of paper, to 11.9 g/g. This improvement was consistent with a drastic increase in porosity, and it was not detrimental to paper strength.
Keywords: Cellulose; Cross-linking; Kraft pulp; Poly(vinyl alcohol); Pulp and paper.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThere are no significant competing interest that could have influenced this work.
Figures
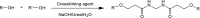



References
-
- Aguado R, Moral A, Mutjé P, Tijero A. Rapeseed stalks for papermaking: studies on pulping, refining and dewatering. Cellul Chem Technol. 2015;49:833–839.
-
- Aguado R, Lourenço AF, Ferreira PJT, et al. The relevance of the pretreatment on the chemical modification of cellulosic fibers. Cellulose. 2019;26:5925–5936. doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02517-7. - DOI
-
- Baptista JGC, Rodrigues SPJ, Matsushita AFY, et al. Does poly(vinyl alcohol) act as an amphiphilic polymer? An interaction study with simvastatin. J Mol Liq. 2016;222:287–294. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.07.025. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
