The Effect of Dysglycaemia on Changes in Pulmonary and Aerobic Function in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 35431976
- PMCID: PMC9005891
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.834664
The Effect of Dysglycaemia on Changes in Pulmonary and Aerobic Function in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
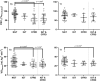
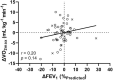
Cross-sectional studies have reported lower pulmonary and aerobic function during exercise in people with cystic fibrosis-related diabetes (CFRD) compared to non-CFRD counterparts. However, this association has yet to be longitudinally investigated. Therefore, this study examines these differences over time between people with cystic fibrosis (CF) of differing glycaemic status. Annual review data, including cardiopulmonary exercise tests and pulmonary function tests, were retrospectively analysed at baseline (T0, n = 82) and at a one-year follow-up (T1, n = 54). Data was analysed in three groups: normal glucose tolerance (NGT), impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), and CFRD. Further analyses were undertaken, with a dichotomous split of NGT and a combined IGT/CFRD group. At baseline, a significant reduction in the majority of variables, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), was observed in the CFRD (n = 19) group compared to NGT (n = 58). At follow-up, no significant differences were observed, and no interaction effect between CFRD status and time was identified. FEV1 and VO2max presented with varying directions and magnitudes of change within patients. In summary, patients with CFRD have a reduced aerobic and pulmonary function compared to non-CFRD counterparts, although such changes disappeared at follow up. Varying responses for FEV1 and VO2max highlight the need to consider both variables as independent markers of function in CF.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory fitness; cystic fibrosis related diabetes; longitudinal data; oxygen uptake; pulmonary disease.
Copyright © 2022 Tomlinson, Stoate, Dobson and Williams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. (1997). Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabet. Care 20 1183–1197. - PubMed
-
- Arena R., Myers J., Aslam S. S., Varughese E. B., Peberdy M. A. (2004). Peak VO2 and VE/VCO2 slope in patients with heart failure: a prognostic comparison. Am. Heart J. 147 354–360. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N., Welsman J. R. (1994). Assessment and interpretation of aerobic fitness in children and adolescents. Exer. Sport Sci. Rev. 22 435–476. - PubMed
-
- Causer A. J., Shute J. K., Cummings M. H., Shepherd A. I., Bright V., Connett G., et al. (2018). Cardiopulmonary exercise testing with supramaximal verification produces a safe and valid assessment of VO2max in people with cystic fibrosis: a retrospective analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 125 1277–1283. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00454.2018 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

