Choroidal Vascularity Index Changes After Exercise in Patients With Glaucoma
- PMID: 35432003
- PMCID: PMC9006879
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.844795
Choroidal Vascularity Index Changes After Exercise in Patients With Glaucoma
Abstract
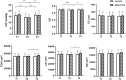
Purpose: To investigate the changes in choroidal vascular structures after exercise in patients with glaucoma using an image binarisation algorithm with enhanced-depth imaging optical coherence tomography. Methods: Thirty-four eyes of 19 patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and 40 eyes of 20 normal subjects were included in the glaucoma and control groups, respectively. All subjects were evaluated before, immediately after, and 30 min after 20-min running at moderate speed. The subfoveal choroidal area was segmented into the luminal area (LA) and stromal area (SA), and the choroidal vascularity index (CVI) was measured by calculating the ratio of LA to the total choroidal area (TCA). The mean intraocular pressure (IOP), subfoveal choroidal thickness, CVI, SA, CA, and TCA were compared within and between both groups. The correlation between CVI, IOP, and other vascular indexes was investigated. Results: In the glaucoma group, a significantly lower CVI was found immediately after exercise and recovered 30 min after exercise. Higher TCA and LA levels were demonstrated 30 min after exercise compared to immediately after exercise. In both groups, IOP decreased immediately after exercise but was restored after a 30-min rest. In the glaucoma group, there was a higher correlation between CVI and other choroidal vascular parameters than in the control group. There was no difference in IOP or choroidal parameters between the groups at different time points. Conclusion: In patients with glaucoma, CVI decreased significantly immediately after exercise, indicating that the choroidal layer is affected by exercise and an unhealthy vascular regulatory mechanism.
Keywords: choroidal vascularity index; exercise; glaucoma; optical coherence tomography; primary open-angle glaucoma.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Fang, Gao, Wu, Qiao, Ruan, Lian, Cen, Fu, Shen and Nie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Choroidal vascularity index changes during the Valsalva manoeuvre in healthy volunteers.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2022 Mar;42(2):367-375. doi: 10.1111/opo.12935. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2022. PMID: 34913506
-
The Effect of Latanoprost on Choroidal Vascularity Index in Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension.J Glaucoma. 2022 Dec 1;31(12):972-978. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000002097. Epub 2022 Aug 9. J Glaucoma. 2022. PMID: 35980849
-
Effects of age and binarising area on choroidal vascularity index in healthy eyes: an optical coherence tomography study.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar;41(3):825-834. doi: 10.1007/s10792-020-01636-6. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33170421
-
Associations Between the Choroidal Vascularity Index and Malignant Glaucoma After Trabeculectomy for Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 8;8:747720. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.747720. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34957140 Free PMC article.
-
Use of choroidal vascularity index for choroidal structural evaluation in smokers: an optical coherence tomography study.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2020 Dec;39(4):298-303. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2020.1793162. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32623911
Cited by
-
Impact of image averaging on choroidal quantification using swept-source optical coherence tomography.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04189-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40598135 Free PMC article.
-
From bench to behaviour: The role of lifestyle factors on intraocular pressure, neuroprotection, and disease progression in glaucoma.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023 May-Jun;51(4):380-394. doi: 10.1111/ceo.14218. Epub 2023 Mar 19. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36859798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review on the impact of exercise on intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 19;44(1):351. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03216-4. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39160282 Free PMC article.
-
Choroidal vascularity index in different types of central serous chorioretinopathy: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 27;18(7):e0289186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289186. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37498843 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

