Arrhythmic risk stratification in ischemic, non-ischemic and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A two-step multifactorial, electrophysiology study inclusive approach
- PMID: 35432775
- PMCID: PMC8968455
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i3.139
Arrhythmic risk stratification in ischemic, non-ischemic and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A two-step multifactorial, electrophysiology study inclusive approach
Abstract
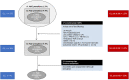
Annual arrhythmic sudden cardiac death ranges from 0.6% to 4% in ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM), 1% to 2% in non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM), and 1% in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Towards a more effective arrhythmic risk stratification (ARS) we hereby present a two-step ARS with the usage of seven non-invasive risk factors: Late potentials presence (≥ 2/3 positive criteria), premature ventricular contractions (≥ 30/h), non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (≥ 1episode/24 h), abnormal heart rate turbulence (onset ≥ 0% and slope ≤ 2.5 ms) and reduced deceleration capacity (≤ 4.5 ms), abnormal T wave alternans (≥ 65μV), decreased heart rate variability (SDNN < 70ms), and prolonged QTc interval (> 440 ms in males and > 450 ms in females) which reflect the arrhythmogenic mechanisms for the selection of the intermediate arrhythmic risk patients in the first step. In the second step, these intermediate-risk patients undergo a programmed ventricular stimulation (PVS) for the detection of inducible, truly high-risk ICM and NICM patients, who will benefit from an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. For HCM patients, we also suggest the incorporation of the PVS either for the low HCM Risk-score patients or for the patients with one traditional risk factor in order to improve the inadequate sensitivity of the former and the low specificity of the latter.
Keywords: Arrhythmias in cardiomyopathy; Arrhythmic sudden cardiac death; Electrophysiology study; Non-invasive risk factors; Risk stratification; Two-step approach.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article. PRESERVE EF is a physician-initiated study that received unrestricted funding by Medtronic Hellas SA.
Figures

References
-
- Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ, Klein H, Wilber DJ, Cannom DS, Daubert JP, Higgins SL, Brown MW, Andrews ML Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial II Investigators. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Kadish A, Dyer A, Daubert JP, Quigg R, Estes NA, Anderson KP, Calkins H, Hoch D, Goldberger J, Shalaby A, Sanders WE, Schaechter A, Levine JH Defibrillators in Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy Treatment Evaluation (DEFINITE) Investigators. Prophylactic defibrillator implantation in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2151–2158. - PubMed
-
- Bayés de Luna A, Coumel P, Leclercq JF. Ambulatory sudden cardiac death: mechanisms of production of fatal arrhythmia on the basis of data from 157 cases. Am Heart J. 1989;117:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Disertori M, Masè M, Ravelli F. Myocardial fibrosis predicts ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017;27:363–372. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

