Effect of Riluzole on the Expression of HCN2 in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons of Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Rats
- PMID: 35432830
- PMCID: PMC9007632
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8313415
Effect of Riluzole on the Expression of HCN2 in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons of Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Rats
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effect of Riluzole on the Expression of HCN2 in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons of Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Rats.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9843721. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843721. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476765 Free PMC article.
Abstract
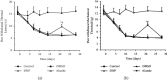
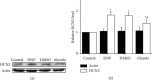
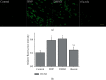
Neuropathic pain since early diabetes swamps patients' lives, and diabetes mellitus has become an increasingly worldwide epidemic. No agent, so far, can terminate the ongoing diabetes. Therefore, strategies that delay the process and the further complications are preferred, such as diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). Dysfunction of ion channels is generally accepted as the central mechanism of diabetic associated neuropathy, of which hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated 2 (HCN2) ion channel has been verified the involvement of neuropathic pain in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Riluzole is a benzothiazole compound with neuroprotective properties on intervention to various ion channels, including hyperpolarization-activated voltage-dependent channels. To investigate the effect of riluzole within lumbar (L3-5) DRG neurons from DNP models, streptozocin (STZ, 70 mg/kg) injection was recruited subcutaneously followed by paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) and paw withdrawal thermal latency (PWTL), which both show significant reduction, whilst relieved by riluzole (4 mg/kg/d) administration, which was performed once daily for 7 consecutive days for 14 days. HCN2 expression was also decreased in line with alleviated behavioral tests. Our results indicate riluzole as the alleviator to STZ-induced DNP with involvement of downregulated HCN2 in lumbar DRG by continual systemic administration in rats.
Copyright © 2022 Dong-mei Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bonhof G. J., Herder C., Strom A. Emerging Biomarkers, Tools, and Treatments for Diabetic Polyneuropathy . Endocr Rev; 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

