Effects of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Combined with Needle-Knife on Pain and Lumbar Function in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation
- PMID: 35432832
- PMCID: PMC9010147
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9185384
Effects of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Combined with Needle-Knife on Pain and Lumbar Function in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Combined with Needle-Knife on Pain and Lumbar Function in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9848054. doi: 10.1155/2023/9848054. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37829360 Free PMC article.
Abstract
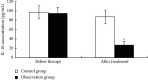
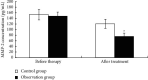
This study aimed for the analysis of the effect of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with needle-knife on pain and lumbar function in patients with lumbar disc herniation. From June 2019 to February 2021, the medical records of 126 patients with lumbar disc herniation admitted to the department of orthopedics of our hospital were selected and divided into the control group (n = 63) treated with acupuncture and moxibustion and the observation group (n = 63) treated with acupuncture and moxibustion combined with needle-knife according to different treatment regimens. After 4 weeks of treatment, the clinical efficacy, pain status, and lumbar function were compared between the two groups. The concentrations of relevant inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, and MMP-2) in peripheral blood of the two patients before and after treatment were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). After treatment, the overall response rate was 93.65% in the observation group, which was higher than 80.95% in the control group (P < 0.05); the visual blurred score (VAS) scores of lower limbs and waist in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, while the expression of pain mediators serotonin (5-HT) and prostaglandin E2 (PEG2) was also lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05); the Oswestry disability index (ODI) in the observation group was lower than that in the control group, while the Japanese Orthopedic Association assessment treatment score (JOA) was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, the concentration levels in peripheral blood (IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, and MMP-2) were significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group (P < 0.05). Acupuncture and moxibustion combined with needle-knife is effective in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation, which helps to improve the clinical efficacy, relieve pain symptoms, promote the improvement of lumbar function, and contribute to the reduction of inflammatory factors.
Copyright © 2022 Guoqiang Peng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Warming Needle Moxibustion Relieves Symptoms of Lumbar Disc Herniation Patients and Upregulates Plasma β-endorphin].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Aug 25;43(8):512-5. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170736. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 30232855 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
The effect of warm needle moxibustion on lumbar disc herniation.Am J Transl Res. 2021 May 15;13(5):5059-5065. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34150092 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of administration of acupuncture stimulation combined with Gushen Zhuyu Decoction on lumbar function in patients with disc herniation].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Oct 25;47(10):907-13. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210951. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36301169 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Efficacy of Warm Needle Moxibustion on Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Meta-Analysis.J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2016 Oct;21(4):311-9. doi: 10.1177/2156587215605419. Epub 2015 Sep 15. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 26378088 Review.
-
[Visualization analysis of CiteSpace knowledge map for lumbar disc herniation treated with acupuncture and moxibustion].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017 May 12;37(5):545-548. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2017.05.024. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017. PMID: 29231618 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of ultrasound-guided percutaneous flexor retinaculum release of the ankle: an anatomical study.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jun 1;14(6):3875-3886. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-81. Epub 2024 May 15. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38846301 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pestle needle combined with six healing sounds Qi Gong on inflammatory factors in patients with lumbar disc herniation.J Med Biochem. 2025 Jun 13;44(3):422-431. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-55195. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40821634 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Effects of Acupuncture and Moxibustion Combined with Needle-Knife on Pain and Lumbar Function in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9848054. doi: 10.1155/2023/9848054. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37829360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang F., Guo D., Sun T., Guan K. A comparative study on short-term therapeutic effects of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy and microendoscopic discectomy on lumbar disc herniation. Pakistan journal of medical sciences . 2019;35(2):426–431. doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.2.650. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jeong J. K., Kim E., Yoon K. S., et al. Acupotomy versus manual acupuncture for the treatment of back and/or leg pain in patients with lumbar disc herniation: A multicenter, randomized, controlled, assessor-blinded clinical trial. Journal of Pain Research . 2020;13:677–687. doi: 10.2147/jpr.s234761. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

