Effect of Comprehensive Nursing Intervention Under Internet-Based WeChat Platform Education on Postoperative Recovery of Puerperae Undergoing Cesarean Section
- PMID: 35432841
- PMCID: PMC9007654
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5040461
Effect of Comprehensive Nursing Intervention Under Internet-Based WeChat Platform Education on Postoperative Recovery of Puerperae Undergoing Cesarean Section
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effect of Comprehensive Nursing Intervention under Internet-Based WeChat Platform Education on Postoperative Recovery of Puerperae Undergoing Cesarean Section.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9792870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9792870. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476789 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of comprehensive nursing intervention under internet-based WeChat platform education on postoperative recovery of puerperae undergoing cesarean section (C-section).
Methods: A total of 96 patients undergoing C-section in our hospital from June 2018 to October 2021 were selected for the retrospective analysis and grouped according to the nursing intervention modes as follows: patients who received a routine nursing intervention were included in the control group, and patients who received comprehensive nursing intervention under internet-based WeChat platform education were included in the study group, with 48 cases each. After the intervention, the postoperative recovery of puerperae undergoing C-section and obstetrics nursing quality were scientifically assessed.
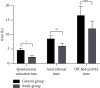
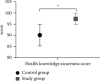
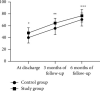
Results: No statistical differences in general data between the two groups were observed (P > 0.05). Compared with the control group, patients in the study group had obviously earlier initial time of lactation (P < 0.05), significantly higher breast milk amount within 48 h after delivery (P < 0.05), significantly earlier spontaneous urination time, anal exhaust time and off-bed activity time (P < 0.05), obviously better mastery of health knowledge (P < 0.05), and, in terms of SCL-90, remarkably lower total score, average total positive score, and the number of positive items and scores in dimensions, such as somatization, obsessive-compulsive, depression, anxiety, interpersonal sensibility, anger-hostility, phobic-anxiety, and paranoid ideation (P < 0.05). At discharge, 3 months, and 6 months of follow-up, patients in the study group obtained significantly higher scores on quality of life than the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: In the nursing of puerperae undergoing C-section, comprehensive nursing intervention measures based on the internet-based WeChat platform education can effectively improve the early lactation, mastery of health knowledge, and adverse emotions of puerpera and promote their postoperative recovery.
Copyright © 2022 Guixiang Kong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retracted: Effect of Comprehensive Nursing Intervention under Internet-Based WeChat Platform Education on Postoperative Recovery of Puerperae Undergoing Cesarean Section.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9792870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9792870. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476789 Free PMC article.
-
WeChat Continuity Nursing on Postpartum Depression and Quality of Life in Primipara Undergoing Cesarean Delivery.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):262-268. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38518146
-
A Study on the Effects of Esketamine Combined with Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Postoperative Pain, Postpartum Depression, and Quality of Life in Women Undergoing Cesarean Section.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Oct;30(10):70-77. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38687857 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Combining Operating Room Nursing Based on Clinical Quantitative Assessment with WeChat Health Education on Postoperative Complications and Quality of Life of Femoral Fracture Patients Undergoing Internal Fixation.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Feb 9;2022:2452820. doi: 10.1155/2022/2452820. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35186223 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of extended care based on Internet and home care platform for orthopaedics after hip replacement surgery in China.J Clin Nurs. 2018 Nov;27(21-22):4077-4088. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14545. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Clin Nurs. 2018. PMID: 29851157
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Application Effect of Multidisciplinary Team Cooperation Model in Chronic Heart Failure under WeChat Platform.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Aug 25;2022:4051955. doi: 10.1155/2022/4051955. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9835236. doi: 10.1155/2023/9835236. PMID: 36059410 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
'Internet+' comprehensive nursing training course in the post-epidemic era-an exploration of the mixed teaching mode: a randomized trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 28;10:1152732. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1152732. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37448807 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Nursing Intervention Based on Network Interactive in Early Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Apr 14;16:1055-1062. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S405442. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37082615 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Effect of Comprehensive Nursing Intervention under Internet-Based WeChat Platform Education on Postoperative Recovery of Puerperae Undergoing Cesarean Section.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9792870. doi: 10.1155/2023/9792870. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrera-Gómez A., Luna-Bertos E. D., Ramos-Torrecillas J., Ocaña-Peinado F. M., García-Martínez O., Ruiz C. The effect of epidural analgesia alone and in association with other variables on the risk of cesarean section. Biological Research for Nursing . 2017;19(4):393–398. doi: 10.1177/1099800417706023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zeinab H. E. I. D. A. R. I., Shahnaz K. O. H. A. N. The Comparison of knowledge and attitude of midwifery and nursing students towards natural childbirth and cesarean section. Journal of Midwifery & Reproductive Health . 2015;3(4)
-
- Ali A., Vahid S., Nehleh P., Mehran F., Hamid R. D., Ayda B. Comparative effect of nature-based sounds intervention and headphones intervention on pain severity after cesarean section: a prospective double-blind randomized trial. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress . 2019;9 doi: 10.5812/aapm.67835. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

