AIM2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation via the MAPK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35432843
- PMCID: PMC9010154
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8756844
AIM2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation via the MAPK Signaling Pathway
Retraction in
-
Retracted: AIM2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation via the MAPK Signaling Pathway.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9839615. doi: 10.1155/2023/9839615. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37388128 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) is a highly prevalent tumor type. The dysregulated expression of melanoma deficiency factor 2 (AIM2) has been observed in a range of tumor types. Herein, we explore the role of AIM2 in the regulation of GC progression.
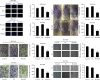
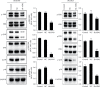
Methods: Gastric cancer cells BGC-823 and MGC-803 in logarithmic growth phase were divided into blank group (control), Control group (NC) and SH-AIM2 group, respectively. Control group and SH-AIM2 group were transfected with AIM2 NC and SH-AIM2, respectively. Nude mice were divided into blank group (control) and SH-AIM2 group, and the treatment methods were the same as above. Differential AIM2 expression in GC tissues was assessed via bioinformatics analyses, after which western blotting was used for analyzing the AIM2 levels in tumor and paracancerous tissues from five stomach cancer patients. In addition, qPCR and protein imprinting were used to assess AIM2 expression levels in GC cells, and AIM2 knockdown was conducted in MGC-803 and BGC-823cells, after which colony formation and EdU incorporation assay were utilized to assess cell proliferation. The oncogenic role of AIM2 was then assessed in mice and validated through immunohistochemical analyses.
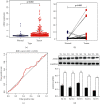
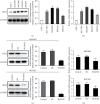
Results: GC tissues and cell lines exhibited marked AIM2 overexpression. AIM2 knockdown significantly impaired GC cell proliferation and migration, as confirmed through in vitro assays. In vivo experiments showed that both the increment ability and invasion and migration ability of AIM2 knockdown group were significantly lower than that of control and NC the change of AIM2 protein level would affect the change of MAPK pathway related protein level.
Conclusions: AIM2 knockdown markedly suppresses the proliferation, migration, as well as invasion of GC cells via the inhibition of MAPK signaling, thereby slowing tumor progression. Overall, these results suggest that further analyses of AIM2 may offer clinically valuable insights that can aid in the treatment of human GC.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaojia Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCL19 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through the CCL19/CCR7/AIM2 pathway.Hum Cell. 2020 Oct;33(4):1120-1132. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00375-1. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 32564199
-
Effect of KIF22 on promoting proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells via MAPK-ERK pathways.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Apr 20;133(8):919-928. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000742. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 32187050 Free PMC article.
-
Absent in melanoma 2 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via inactivation of AKT signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 15;11(1):8235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87744-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33859277 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Feb;25(2):53. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12569. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34913077 Free PMC article.
-
AIM2 promotes the progression of HNSCC via STAT1 mediated transcription and IL-17/MAPK signaling.Cell Signal. 2025 Mar;127:111545. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111545. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Cell Signal. 2025. PMID: 39638137
Cited by
-
The dual roles of human PYHIN family proteins in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2025 May 2;16:1576674. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576674. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40386782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AIM2 and Psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 18;14:1085448. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1085448. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36742336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis related genes and prognosis of gastric cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct 24;14(10):373-399. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i10.373. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37970110 Free PMC article.
-
Increased copy number of imprinted genes in the chromosomal region 20q11-q13.32 is associated with resistance to antitumor agents in cancer cell lines.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Dec 2;14(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01368-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36461044 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: AIM2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation via the MAPK Signaling Pathway.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9839615. doi: 10.1155/2023/9839615. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37388128 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

