Effects of Insulin Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Assisted Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Oxidative Stress State, Cell Adhesion Factor, and Pregnancy Outcome of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 35432844
- PMCID: PMC9007655
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5330134
Effects of Insulin Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Assisted Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Oxidative Stress State, Cell Adhesion Factor, and Pregnancy Outcome of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Insulin Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Assisted Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Oxidative Stress State, Cell Adhesion Factor, and Pregnancy Outcome of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9864923. doi: 10.1155/2023/9864923. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476807 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: The changes of oxidative stress state, cell adhesion factor (sICAM-1) level, blood glucose, and blood lipid of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) assisted by insulin combined with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescription were detected to explore the effect of TCM treatment on maternal and infant outcomes of GDM.
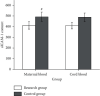
Methods: A total of 60 patients diagnosed with GDM from January 2019 to December 2019 were selected. Among them, 30 patients were treated with insulin combined with TCM prescription (control group), and 30 patients were treated with nursing intervention based on control group (study group). Serum of maternal vein and fetal umbilical vein was collected. The contents of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and lipid oxide (MDA) were determined. The content of intercellular adhesion factor (ICAM-1) was measured, and the differences of fasting blood glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (CHO) and low density lipoprotein (LDL-C) between 2 groups were compared. The incidence of maternal and infant adverse outcomes was assessed.
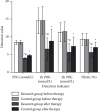
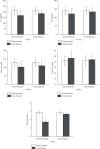
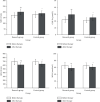
Results: After treatment, blood glucose indexes in 2 groups were decreased, and the study group was lower than the control group. After treatment, LDL-C, TC and TG in 2 groups were lower than before, and the study group was lower than the control group. HDL-C was higher than before treatment, and the study group was higher than the control group. After treatment, oxidation-related substances SOD and GSH-Px in 2 groups were higher than before, and those in study group were higher than those in control group. ROS and MDA were lower than before treatment, and the level of sICAM-1 in the study group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Clinical application of insulin combined with TCM prescription assisted comprehensive nursing intervention in the treatment of gestational diabetes, pregnancy outcome is improved.
Conclusions: Oxidative stress imbalance exists in GDM and the causes of adverse pregnancy outcomes are closely related to oxidative stress and vascular endothelial injury. TCM can improve the oxidative stress imbalance and the pregnancy outcome of patients with GDM from the perspective of reducing vascular endothelial injury. Comprehensive nursing intervention for pregnant women with GDM can optimize the outcome of pregnancy and is worthy of clinical application.
Copyright © 2022 Yanling Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation of Homocysteine, AHSG, CRP with Insulin Resistance, 25-(OH)2-VitD, Blood Lipids in Gestational Diabetes Patients.Clin Lab. 2021 Feb 1;67(2). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.200609. Clin Lab. 2021. PMID: 33616345
-
Application Value of Predictive Model Based on Maternal Coagulation Function and Glycolipid Metabolism Indicators in Early Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Front Public Health. 2022 Mar 21;10:850191. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.850191. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35387184 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3) in serum of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and its relationship with insulin resistance.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Dec;21(24):5702-5710. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201712_14016. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29272006
-
Clinical efficacies, underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of Chinese medicines for diabetic nephropathy treatment and management.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Sep;11(9):2749-2767. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34589395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Probiotic Supplement in Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Sep 5;2019:5364730. doi: 10.1155/2019/5364730. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31583250 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Effects of Insulin Combined with Traditional Chinese Medicine Assisted Comprehensive Nursing Intervention on Oxidative Stress State, Cell Adhesion Factor, and Pregnancy Outcome of Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9864923. doi: 10.1155/2023/9864923. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang H., Wei Y., Gao X., et al. Risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women—a prospective study of 16 286 pregnant women in China. Diabetic Medicine . 2009;26(11):1099–1104. - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D., Snell-Bergeon J. K., Hartsfield C. L., Bischoff K. J., Hamman R. F., McDuffie R. S. Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) over time and by birth cohort: kaiser Permanente of Colorado GDM Screening Program. Diabetes Care . 2005;28(3):579–584. - PubMed
-
- Seshiah V., Balaji V., Balaji M. S., Sanjeevi C., Green A. Gestational diabetes mellitus in India. Japi . 2004;52(9):707–711. - PubMed
-
- Association AD. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care . 2004;27(1):88–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

