Selective covalent targeting of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by enantiopure chlorofluoroacetamide
- PMID: 35432850
- PMCID: PMC8905997
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc06596c
Selective covalent targeting of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by enantiopure chlorofluoroacetamide
Abstract
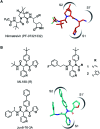
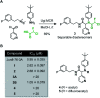
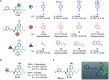
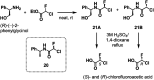
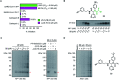
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has necessitated the development of antiviral agents against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The main protease (Mpro) is a promising target for COVID-19 treatment. Here, we report an irreversible SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor possessing chlorofluoroacetamide (CFA) as a warhead for the covalent modification of Mpro. Ugi multicomponent reaction using chlorofluoroacetic acid enabled the rapid synthesis of dipeptidic CFA derivatives that identified 18 as a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. Among the four stereoisomers, (R,R)-18 exhibited a markedly higher inhibitory activity against Mpro than the other isomers. Reaction kinetics and computational docking studies suggest that the R configuration of the CFA warhead is crucial for the rapid covalent inhibition of Mpro. Our findings highlight the prominent influence of the CFA chirality on the covalent modification of proteinous cysteines and provide the basis for improving the potency and selectivity of CFA-based covalent inhibitors.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou P. Yang X.-L. Wang X.-G. Hu B. Zhang L. Zhang W. Si H.-R. Zhu Y. Li B. Huang C.-L. Chen H.-D. Chen J. Luo Y. Guo H. Jiang R.-D. Liu M.-Q. Chen Y. Shen X.-R. Wang X. Zheng X.-S. Zhao K. Chen Q.-J. Deng F. Liu L.-L. Yan B. Zhan F.-X. Wang Y.-Y. Xiao G.-F. Shi Z.-L. Nature. 2020;579:270–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

