Formulation and production of persimmon milk drink and evaluation of its physicochemical, rheological, and sensorial properties
- PMID: 35432960
- PMCID: PMC9007307
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2772
Formulation and production of persimmon milk drink and evaluation of its physicochemical, rheological, and sensorial properties
Abstract
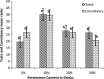
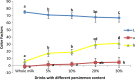
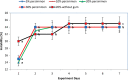
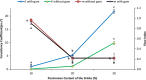
One of the effective ways for increasing milk intake in a diet is producing flavored milk. In the present study, flavored persimmon milk drinks were formulated and produced. Rheological, sensorial, and physicochemical properties of the drinks were evaluated. Different amounts of persimmon (5, 10, 20, and 30% W/V), gum Arabic (0.1 and 0.2% W/V), and sugar (3 and 5% W/V) were used to produce persimmon milk. All the experiments were done in a completely randomized design (CRD) in three replicates. First, persimmons were mixed thoroughly in a blender then, according to the formulation, whole milk was added to it and mixed again. The obtained mixture was heated up to 50 ᵒC then sugar and the gum were added and mixed completely for 3 min. The drink was pasteurized at 90 ᵒC for 1 min. Sensorial analysis revealed that the most acceptable persimmon milk was related to 0.1% gum Arabic, 5% sugar, and 10% persimmon. Flow behavior of the drinks with 20 and 30% persimmon was Non-Newtonian, while 10% persimmon samples with and without gum showed Newtonian behavior. The drinks with 20 and 30% persimmon were pseudoplastic, and their apparent viscosity increased by increasing shear rates. By applying a proper content of persimmon in milk, we can produce a nutritious flavored milk drink with acceptable taste, stability, and consistency. As this drink has high nutrient contents like phenol, dietary fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, etc., it can help promote health, especially for children.
Keywords: drink; formulation; persimmon milk; physicochemical; rheology; sensorial properties.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in the present research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of gum tragacanth on rheological and physical properties of a flavored milk drink made with date syrup.J Dairy Sci. 2013 Aug;96(8):4794-803. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5942. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Dairy Sci. 2013. PMID: 23746580
-
Neutralized Direct-Acid-Set Whey as an Extender for a Chocolate-Flavored Dairy Drink 1.J Food Prot. 1982 Jan;45(1):12-13. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-45.1.12. J Food Prot. 1982. PMID: 30866347
-
Effect of in situ exopolysaccharide production on physicochemical, rheological, sensory, and microstructural properties of the yogurt drink ayran: an optimization study based on fermentation kinetics.J Dairy Sci. 2015 Mar;98(3):1604-24. doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8936. Epub 2014 Dec 26. J Dairy Sci. 2015. PMID: 25547308
-
The association of flavored milk consumption with milk and energy intake, and obesity: A systematic review.Prev Med. 2018 Jun;111:151-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Prev Med. 2018. PMID: 29501475
-
Effect of flavored milk vs plain milk on total milk intake and nutrient provision in children.Nutr Rev. 2016 Jan;74(1):1-17. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv031. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Nutr Rev. 2016. PMID: 26534904 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of storage on the physicochemical, rheological, antioxidant activity, and sensory properties of soy whey-fortified pineapple juice beverages.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 May 27;12(8):5858-5871. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4219. eCollection 2024 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39139946 Free PMC article.
-
Physico-Chemical Property, Sensory Profile and Consumer Acceptability of Water Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis L.) Chocolate Milk Using Alkalized and Natural Cocoa Powder.Foods. 2023 Apr 26;12(9):1797. doi: 10.3390/foods12091797. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37174335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu‐Jdayil, B. , Mohameed, H. A. , & Eassa, A. (2004). Rheology of wheat starch‐milk‐sugar systems: Effect of starch concentration, sugar type and concentration, and milk fat content. Journal of Food Engineering, 64(2), 207–212. 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2003.09.034 - DOI
-
- Altuntas, E. , Cangi, R. , & Kaya, C. (2011). Physical and chemical properties of persimmon fruit. International Agrophysics, 25(1), 89–92.
-
- Barnes, H. A. (2000). A handbook of elementary rheology. Univ. of Wales, Institute of Non‐Newtonian Fluid Mechanics.
-
- Bourne, M. C. (2002). Food texture and viscosity concept and measurement, 2nd ed. Academic Press.
-
- Branger, E. B. , Sims, C. A. , Schmidt, R. , Okeefe, S. F. , & Cornell, J. A. (1999). Sensory characteristics of cottage cheese whey and grapefruit juice blends and changes during processing. Journal of Food Science, 64(1), 180–184. 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1999.tb09887.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials