Effect of oligonol, a lychee-derived polyphenol, on skeletal muscle in ovariectomized rats by regulating body composition, protein turnover, and mitochondrial quality signaling
- PMID: 35432979
- PMCID: PMC9007287
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2750
Effect of oligonol, a lychee-derived polyphenol, on skeletal muscle in ovariectomized rats by regulating body composition, protein turnover, and mitochondrial quality signaling
Abstract
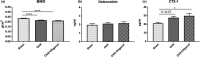
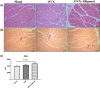
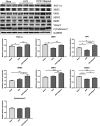
Oligonol is a low-molecular-weight polyphenol product derived from lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) fruits. This study was focused on the effects of oligonol on the skeletal muscle of ovariectomized rats. We randomly divided female Sprague-Dawley rats into three groups: a sham surgery control group (Sham), an ovariectomy (OVX) group, and an OVX group treated with oligonol (OVX + Oligonol). Oligonol was intraperitoneally administrated at 30 mg/kg daily for 6 weeks. Oligonol treatment after OVX decreased body weight and fat mass, regulated lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle, without loss of lean mass and bone. Bone turnover was not affected by oligonol. In protein synthesis and degradation, oligonol increased the levels of the mammalian target of rapamycin and its downstream targets, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 and 70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase, and it stimulated the expression of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway proteins, the forkhead box transcription factors of the class O and the muscle ring-finger protein-1. Moreover, oligonol treatment enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics. Thus, our results indicated that oligonol treatment had beneficial effects on the skeletal muscle in an estrogen-deficiency rat model.
Keywords: body composition; mitochondrial dynamics; ovariectomy; polyphenols; skeletal muscle.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bahijri, S. M. , Ajabnoor, G. , Hegazy, G. A. , Alsheikh, L. , Moumena, M. Z. , Bashanfar, Bu. M. , & Alzahrani, A. H. (2018). Supplementation with oligonol, prevents weight gain and improves lipid profile in overweight and obese Saudi females. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 14, 164–170. 10.2174/1573401313666170609101408 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, Y. C. , Chen, Y. T. , Liu, H. W. , Chan, Y. C. , Liu, M.‐Y. , Hu, S.‐H. , Tseng, W.‐T. , Wu, H.‐L. , Wang, M.‐F. , & Chang, S.‐J. (2019). Oligonol alleviates sarcopenia by regulation of signaling pathways involved in protein turnover and mitochondrial quality. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63, e1801102. 10.1002/mnfr.201801102 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Collins, B. C. , Arpke, R. W. , Larson, A. A. , Baumann, C. W. , Xie, N. , Cabelka, C. A. , Nash, N. L. , Juppi, H.‐K. , Laakkonen, E. K. , Sipilä, S. , Kovanen, V. , Spangenburg, E. E. , Kyba, M. , & Lowe, D. A. (2019). Estrogen regulates the satellite cell compartment in females. Cell Reports, 28(368–381), e366. 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

