Novel Insight into the Concept of Favorable Combination of Electrodes in High Voltage Supercapacitors: Toward Ultrahigh Volumetric Energy Density and Outstanding Rate Capability
- PMID: 35433029
- PMCID: PMC8995712
- DOI: 10.1002/gch2.202100139
Novel Insight into the Concept of Favorable Combination of Electrodes in High Voltage Supercapacitors: Toward Ultrahigh Volumetric Energy Density and Outstanding Rate Capability
Abstract
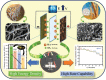
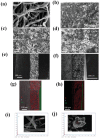
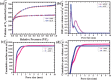
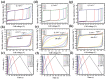
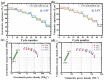
Most of the biomass-derived carbon-based supercapacitors using organic electrolytes exhibit very low energy density due to their low operating potential range between 2.7 and 3.0 V. A novel insight into the concept of the different porous architecture of electrode materials that is employed to extend a device's operating potential up to 3.4 V using TEABF4 in acetonitrile, is reported. The combination of two high surface area activated carbons derived from abundant natural resources such as industrial waste cotton and wheat flour as sustainable and green carbon precursors is explored as an economical and efficient supercapacitor carbon electrode. Benefitting from the simultaneous achievement of the higher potential window (3.4 V) with higher volumetric capacitance (101 F cm-3), the supercapacitor electrodes exhibit higher volumetric energy density (42.85 Wh L-1). Bimodal pore size distribution of carbon with a tuned pore size and high specific surface area of the electrode can promote the fast transport of cations and anions. Hence, it exhibits a high rate capability even at 30 A g-1. In addition, the electrodes remain stable during operation cell voltage at 3.4 V upon 15 000 charging-discharging cycles with 90% capacitance retention.
Keywords: carbons; high durability; supercapacitors; volumetric capacitance; volumetric energy density.
© 2022 The Authors. Global Challenges published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Staaf L. G. H., Lundgren P., Enoksson P., Nano Energy 2014, 9, 128.
-
- Abioye A. M., Ani F. N., Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1282.
-
- Lu H., Zhao X. S., Sustainable Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1265.
-
- Kim C., Moon J. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19682. - PubMed
-
- Liu C. F., Liu Y. C., Yi T. Y., Hu C. C., Carbon 2019, 145, 529.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

