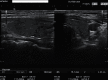
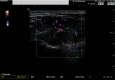
Two Case Reports of Subacute Thyroiditis after Receiving Vaccine for COVID-19
- PMID: 35433060
- PMCID: PMC9008488
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3180004
Two Case Reports of Subacute Thyroiditis after Receiving Vaccine for COVID-19
Abstract
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, caused by a coronavirus named SARS-CoV-2, has struck the planet with great force. As of December 2019, the virus has made its devasting route across all continents . In January 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) registered over 5.5 million COVID-19 related deaths. Most of these people had suffered from pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome , and in some cases, extensive damage to all organ systems. To get hold of this pandemic, it was vital to find effective vaccines against it. The two vaccine candidates BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) and ChAdOx1 (University of Oxford and AstraZeneca) offer a high level of protection against COVID-19 by providing immunity due to antibody production against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. In addition to general side effects, immunological side effects such as subacute thyroiditis can follow the vaccination. This transient inflammatory condition of the thyroid gland is characterized with hyperthyroxinemia, inflammation, pain, and tenderness in the thyroid region, as well as an elevation of serum thyroglobulin concentration. There are only a few reports on the occurrence of this disease after receiving a COVID-19 vaccine. We present two cases of subacute thyroiditis after vaccination with the vaccines BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 and try to enlighten the problem of immunological phenomena after vaccination. It must be discussed whether cross-reactivity of the spike protein and tissue proteins such as thyroid peroxidase (TPO), an "autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome by adjuvants" (ASIA), or the circulating spike protein itself after vaccination are responsible for the SAT.
Copyright © 2022 Jan Adelmeyer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Pfizer/BioNTech and Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines against COVID-19 morbidity and mortality in real-world settings at countrywide vaccination campaign in Saudi Arabia.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Nov;25(22):7185-7191. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202111_27271. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34859883
-
Thyroiditis following vaccination against COVID-19: Report of two cases and review of the literature.Metabol Open. 2021 Dec;12:100136. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100136. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34693241 Free PMC article.
-
Subacute thyroiditis following COVID-19 vaccination: Case presentation.Antivir Ther. 2023 Oct;28(5):13596535231208831. doi: 10.1177/13596535231208831. Antivir Ther. 2023. PMID: 37861754
-
Development of Graves' Disease After SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 23;9:778964. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.778964. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34888290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid as a target of adjuvant autoimmunity/inflammatory syndrome due to mRNA-based SARS-CoV2 vaccination: from Graves' disease to silent thyroiditis.J Endocrinol Invest. 2022 Apr;45(4):875-882. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01707-0. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022. PMID: 34792795 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 vaccination and thyroiditis.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jul;37(4):101759. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2023.101759. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36933997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid Function in the Time of COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Disease Progression and Vaccination Effect.Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Oct 27;22(3):e146857. doi: 10.5812/ijem-146857. eCollection 2024 Jul. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 40735669 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into SARS-CoV-2-associated subacute thyroiditis: from infection to vaccine.Virol J. 2023 Jun 21;20(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02103-1. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37344878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Triggle C. R., Bansal D., Ding H., et al. A comprehensive review of viral characteristics, transmission, pathophysiology, immune response, and management of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 as a basis for controlling the pandemic. Frontiers in Immunology . 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.631139.631139 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Organisation W. H. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard . 2022. https://covid19.who.int22.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous