Research Advances on Matrine
- PMID: 35433636
- PMCID: PMC9010661
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.867318
Research Advances on Matrine
Abstract
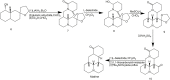
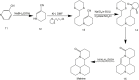
Matrine is an alkaloid extracted from traditional Chinese herbs including Sophora flavescentis, Sophora alopecuroides, Sophora root, etc. It has the dual advantages of traditional Chinese herbs and chemotherapy drugs. It exhibits distinct benefits in preventing and improving chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and tumors. The review introduced recent research progresses on extraction, synthesis and derivatization of Matrine. The summary focused on the latest research advances of Matrine on anti-atherosclerosis, anti-hypertension, anti-ischemia reperfusion injury, anti-arrhythmia, anti-diabetic cardiovascular complications, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterium, anti-virus, which would provide new core structures and new insights for new drug development in related fields.
Keywords: derivatization; extraction; matrine; molecular mechanism; pharmacological effects; synthesis.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Jia, Rong, Zhou, Cao, Li, Guo, Jin, Wang, Huang, Li, He, Li, Ma, Lv, Shao, Zhang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors A-HL and H-LC are employed by Shaanxi Pharmaceutical Holding Group Co., LTD, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bohlmann F., Rahtz D., Arndt C. (2010). Lupinen‐Alkaloide, XI. Die Alkaloide aus Sophora flavescens. Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 91 (10), 2189–2193. 10.1002/cber.19580911026 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources