A Rapid, Highly Sensitive and Open-Access SARS-CoV-2 Detection Assay for Laboratory and Home Testing
- PMID: 35433827
- PMCID: PMC9011764
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.801309
A Rapid, Highly Sensitive and Open-Access SARS-CoV-2 Detection Assay for Laboratory and Home Testing
Abstract
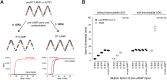
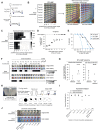
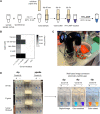
RT-qPCR-based diagnostic tests play important roles in combating virus-caused pandemics such as Covid-19. However, their dependence on sophisticated equipment and the associated costs often limits their widespread use. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification after reverse transcription (RT-LAMP) is an alternative nucleic acid detection method that overcomes these limitations. Here, we present a rapid, robust, and sensitive RT-LAMP-based SARS-CoV-2 detection assay. Our 40-min procedure bypasses the RNA isolation step, is insensitive to carryover contamination, and uses a colorimetric readout that enables robust SARS-CoV-2 detection from various sample types. Based on this assay, we have increased sensitivity and scalability by adding a nucleic acid enrichment step (Bead-LAMP), developed a version for home testing (HomeDip-LAMP), and identified open-source RT-LAMP enzymes that can be produced in any molecular biology laboratory. On a dedicated website, rtlamp.org (DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.6033689), we provide detailed protocols and videos. Our optimized, general-purpose RT-LAMP assay is an important step toward population-scale SARS-CoV-2 testing.
Keywords: COVID-19 diagnostics; RT-LAMP; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; isothermal amplification; open-source.
Copyright © 2022 Kellner, Ross, Schnabl, Dekens, Matl, Heinen, Grishkovskaya, Bauer, Stadlmann, Menéndez-Arias, Straw, Fritsche-Polanz, Traugott, Seitz, Zoufaly, Födinger, Wenisch, Zuber, Vienna COVID-19 Detection Initiative (VCDI), Pauli and Brennecke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anahtar M. N., McGrath G. E. G., Rabe B. A., Tanner N. A., White B. A., Lennerz J. K. M., et al. (2021). Clinical Assessment and Validation of a Rapid and Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 Test Using Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification without the Need for RNA Extraction. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 8 (2), ofaa631. 10.1093/ofid/ofaa631 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artesi M., Bontems S., Göbbels P., Franckh M., Maes P., Boreux R., et al. (2020). A Recurrent Mutation at Position 26340 of SARS-CoV-2 Is Associated with Failure of the E Gene Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR Utilized in a Commercial Dual-Target Diagnostic Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58 (10), e01598–20. 10.1128/JCM.01598-20 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baba M. M., Bitew M., Fokam J., Lelo E. A., Ahidjo A., Asmamaw K., et al. (2021). Diagnostic Performance of a Colorimetric RT -LAMP for the Identification of SARS-CoV-2: A Multicenter Prospective Clinical Evaluation in Sub-saharan Africa. EClinicalMedicine 40, 101101. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

