Comparison of Intestinal Microbiota Between Healthy and MMVD Chihuahuas Using 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
- PMID: 35433906
- PMCID: PMC9007596
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.846492
Comparison of Intestinal Microbiota Between Healthy and MMVD Chihuahuas Using 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
Abstract
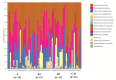
Myxomatous mitral valve disease (MMVD) is the most common cause of congestive heart failure in dogs, and although complications of MMVD to the lungs and kidneys have been identified, complications to the gut are less well understood. The intestinal microbiota is an important factor in the gut, and although the association between heart disease and the intestinal microbiota has been shown in human medicine, it is unknown in dogs. The study aimed to evaluate the relationship between MMVD and gut microbiota. A total of 69 healthy Chihuahuas and Chihuahuas with MMVD were evaluated for cardiac health by echocardiography and chest radiography and grouped according to ACVIM guidelines. Fecal samples were collected from all cases and 16S rRNA sequencing was used to reveal the intestinal microbiota. There were significant differences in LA/Ao, LVIDd, E vel, VHS, and VLAS with the severity of ACVIM. On the other hand, there were no significant differences in the diversity and composition of gut microbiota among the groups. The present study did not identify the effects of MMVD on the gut microbiota.
Keywords: Chihuahua; fractional shortening; intestinal complication; intestinal microbiota; myxomatous mitral valve disease.
Copyright © 2022 Araki, Iwanaga, Ueda, Shima, Ishihara, Aizu, Fukayama and Isaka.
Conflict of interest statement
AS, GI, MA, and TF were employed by Anicom Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen LW, Landow L, Baek L, Jansen E, Baker S. Association between gastric intramucosal pH and splanchnic endotoxin, antibody to endotoxin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Crit Care Med. (1993) 21:210–7. 10.1097/00003246-199302000-00011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tang WH, Wang Z, Fan Y, Levison B, Hazen JE, Donahue LM, et al. . Prognostic value of elevated levels of intestinal microbe-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with heart failure: refining the gut hypothesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 64:1908–14. 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.617 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

