Exploring the mechanisms of action of Cordyceps sinensis for the treatment of depression using network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 35434037
- PMCID: PMC9011256
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-762
Exploring the mechanisms of action of Cordyceps sinensis for the treatment of depression using network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
Background: Depression is the most common type of psychological disorder, with continuous, prolonged, and persistent bad moods as the main clinical feature. Cordyceps sinensis is a complex consisting of the ascospores and bodies of insect larvae from the Hepialidae family that have been parasitized by Cordyceps sinensis militaris. Previous studies have reported that this herb has antidepressant activity. The present study used network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques to investigate the potential antidepressant mechanisms of Cordyceps sinensis.
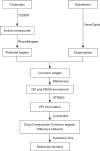
Methods: The active ingredients of Cordyceps sinensis were identified using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP) and the potential targets were predicted using the PharmMapper platform. The GeneCards database was then used to obtain sub-targets for depression. Common targets were screened and enrichment analyses were performed using the Metascape platform. Finally, the relationship between the active ingredients and the core targets were verified by molecular docking.
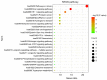
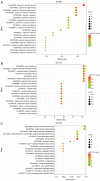
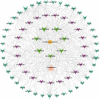
Results: Through network pharmacological analysis, 7 active ingredients in Cordyceps sinensis and 41 common targets of drugs and diseases were identified. The active ingredients of Cordyceps sinensis may exert antidepressant effects by acting on important targets such as catalase (CAT), CREB binding protein (CREBBP), epidermal growth factor (EGF), and E1A binding protein P300 (EP300), and by modulating the signaling pathways in which these targets are involved. Subsequently, the core targets were docked to the active ingredients and good binding was observed.
Conclusions: The active ingredients of Cordyceps sinensis may exert antidepressant effects by regulating the CREB binding protein and anti-oxidative stress effects. The foxo signaling pathway (hsa04068), hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) signaling pathway (hsa04066), and Huntington's disease (hsa05016) may be involved in the underlying mechanisms of Cordyceps sinensis. The joint application of network pharmacology and molecular docking provides a new approach to study the mechanisms of action of traditional Chinese medicine. Cordyceps sinensis may play an important role in the future treatment of patients with depression.
Keywords: Cordyceps sinensis; depression; molecular docking; network pharmacology.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-762/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis Explores the Mechanisms of Cordyceps sinensis in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus.J Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;2022:3156785. doi: 10.1155/2022/3156785. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36072973 Free PMC article.
-
Based on Network Pharmacology Tools to Investigate the Molecular Mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis on the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Feb 5;2021:8891093. doi: 10.1155/2021/8891093. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 33628839 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Study on the Potential Mechanism of Yi-Qi-Huo-Xue-Tong-Luo Formula in Treating Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.J Diabetes Res. 2021 May 28;2021:9941791. doi: 10.1155/2021/9941791. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34159207 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Active Ingredients and Mechanism of Action of Huanglian Huazhuo Capsule for the Treatment of Obese Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 3;2022:2780647. doi: 10.1155/2022/2780647. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36225181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of bailing capsules (cordyceps sinensis) in the treatment of chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis and network pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 5;15:1342831. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1342831. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38645562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of Ophiocordyceps sinensis in the treatment of Hashimoto's thyroiditis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 3;14:1272124. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1272124. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37854714 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Shared Genetic Etiology Between Parkinson's Disease and Depression.J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(3):483-493. doi: 10.3233/JPD-230176. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 38457145 Free PMC article.
-
Druggable Targets for Postpartum Depression: A Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Study.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun 19;45(1):61. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01581-x. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40537683 Free PMC article.
-
The Large Molecular Weight Polysaccharide from Wild Cordyceps and Its Antitumor Activity on H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice.Molecules. 2023 Apr 10;28(8):3351. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083351. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110586 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Sijunzi Decoction Suppresses Gastric Cancer Metastasis via the m6A Methyltransferase METTL14 Based on Untargeted Metabolomics Studies and Network Pharmacology Analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 31;19:2369-2392. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S506702. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40190808 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
