Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin Attenuate Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-1
- PMID: 35434529
- PMCID: PMC9003386
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00207
Canagliflozin and Dapagliflozin Attenuate Glucolipotoxicity-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Cardiomyocytes via Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-1
Abstract
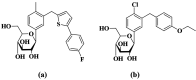
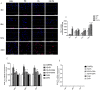
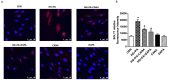
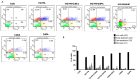
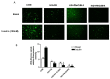
Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2) are recently approved drugs for the treatment of diabetes that regulate blood glucose levels by inhibiting reabsorption of glucose and sodium in the proximal tubules of the kidney. SGLT2 inhibitors have also shown cardiovascular (CV) benefits in diabetic patients. However, the therapeutic efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors with respect to CV disease needs further investigation. Thus, the aim of the present study was to examine the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, canagliflozin (CANA) and dapagliflozin (DAPA) in vitro under glucolipotoxic condition by treating cultured cardiomyocytes (H9C2) with high glucose (HG) and high lipid, palmitic acid (PA), to investigate whether inhibition of sodium glucose cotransporter could prevent any harmful effects of glucolipotoxicity in these cells. SGLT1 expression was measured by immunofluorescence staining and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Oxidative stress and apoptosis were measured by flow cytometry. Hypertrophy was measured by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and crystal violet staining. A significant increase in SGLT1 expression was observed in HG- and PA-treated cardiomyocytes. Also, a significant increase in reactive oxygen species generation and apoptosis was observed in HG+PA-treated cultured cardiomyocytes. HG- and PA-treated cardiomyocytes developed significant structural alterations. All these effects of HG and PA were attenuated by CANA and DAPA. In conclusion, our study demonstrates upregulation of SGLT1 induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in cultured cardiomyocytes. Thus, inhibition of SGLT1 may be used as a possible approach for the treatment of CVD in diabetic patients.
© 2022 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- GH R. P.; Goff D. C. Jr.; Bigger J. T.; Buse J. B.; Cushman W. C.; Genuth S.; Ismail-Beigi F.; Grimm R. H. Jr; Probstfield J. L.; Simons-Morton D. G.; Friedewald W. T. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358 (24), 2545–2559. 10.1056/NEJMoa0802743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
