Crystal structure of plasmoredoxin, a redox-active protein unique for malaria parasites
- PMID: 35434650
- PMCID: PMC9006252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2022.03.004
Crystal structure of plasmoredoxin, a redox-active protein unique for malaria parasites
Abstract
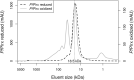
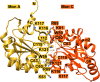
Plasmoredoxin is a 22 kDa thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase involved in cellular redox regulatory processes and antioxidant defense. The 1.6 Å structure of the protein, solved via X-ray crystallography, adopts a modified thioredoxin fold. The structure reveals that plasmoredoxin, unique for malarial parasites, forms a new subgroup of thioredoxin-like proteins together with tryparedoxin, unique for kinetoplastids. Unlike most members of this superfamily, Plrx does not have a proline residue within the CxxC redox motif. In addition, the Plrx structure has a distinct C-terminal domain. Similar to human thioredoxin, plasmoredoxin forms monomers and dimers, which are also structurally similar to the human thioredoxin dimer, and, as in humans, plasmoredoxin is inactive as a dimer. Monomer-dimer equilibrium depends on the surrounding redox conditions, which could support the parasite in reacting to oxidative challenges. Based on structural considerations, the residues of the dimer interface are likely to interact with target proteins. In contrast to human and Plasmodium falciparum thioredoxin, however, there is a cluster of positively charged residues at the dimer interface of plasmoredoxin. These intersubunit (lysine) residues might allow binding of the protein to cellular membranes or to plasminogen. Malaria parasites lack catalase and glutathione peroxidase and therefore depend on their other glutathione and thioredoxin-dependent redox relays. Plasmoredoxin could be part of a so far unknown electron transfer system that only occurs in these parasites. Since the surface charge of plasmoredoxin differs significantly from other members of the thioredoxin superfamily, its three-dimensional structure can provide a model for designing selective redox-modulatory inhibitors.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Bacteroides fragilis, Bf; Crithidia fasciculata, Cf; Disulfide bonds; Human, h; Leishmania major, Lm; Monomer–dimer population; Plasmodium falciparum; Plasmodium falciparum, Pf; Plasmoredoxin; Redox; Thioredoxin; Trx, thioredoxin; Trypanosoma brucei, Tb; Wuchereria bancrofti, Wb; amino acids, aa; glutaredoxin, Grx; glutathione (reduced / oxidized), GSH / GSSG; glutathione reductase, GR; peroxiredoxin Prx, either 2-Cys-Prx or Prx1m; plasmoredoxin, Plrx; thioredoxin reductase, TrxR; trypanothione, Try (reduced, oxidized); tryparedoxin reductase, TR; tryparedoxin, Txn.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



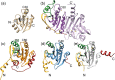



Similar articles
-
Plasmoredoxin, a novel redox-active protein unique for malarial parasites.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Mar;270(6):1057-64. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03495.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12631266
-
Identification of proteins targeted by the thioredoxin superfamily in Plasmodium falciparum.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Apr;5(4):e1000383. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000383. Epub 2009 Apr 10. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19360125 Free PMC article.
-
The thioredoxin antioxidant system.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23899494 Review.
-
The thiol-based redox networks of pathogens: unexploited targets in the search for new drugs.Biofactors. 2006;27(1-4):109-20. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520270110. Biofactors. 2006. PMID: 17012768 Review.
-
Thioredoxin and glutathione systems in Plasmodium falciparum.Int J Med Microbiol. 2012 Oct;302(4-5):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2012.07.007. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Int J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22939033 Review.
References
-
- Alphey M.S., Leonard G.A., Gourley D.G., Tetaud E., Fairlamb A.H., Hunter W.N. The high resolution crystal structure of recombinant Crithidia fasciculata tryparedoxin-I. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:25613–25622. - PubMed
-
- Arnér E.S.J., Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000;267:6102–6109. - PubMed
-
- Becker K., Kanzok S.M., Iozef R., Fischer M., Schirmer R.H., Rahlfs S. Plasmoredoxin, a novel redox-active protein unique for malarial parasites. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003;270:1057–1064. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

