A multimodal nanoparticles-based theranostic method and system
- PMID: 35434929
- PMCID: PMC9541245
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.1796
A multimodal nanoparticles-based theranostic method and system
Abstract
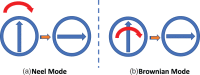
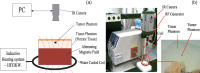
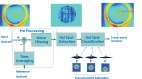
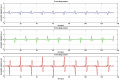
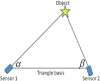
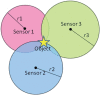
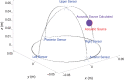
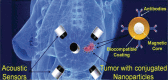
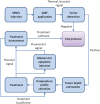
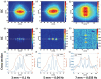
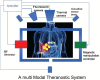
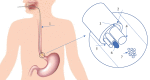
We propose a nanoparticles-based system for the early detection of tumors, treatment under real-time feedback, and monitoring. The building blocks of the system comprise a few modalities that are integrated into one powerful system which can operate at the patient's bedside in an outpatient clinic setting. The method relies on the unique characteristics of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. It takes advantage of their ability to produce acoustical signals under alternating magnetic fields (AMFs) and to produce heat under these same AMFs with different parameters. It utilizes the nanoparticles' coating for specific binding. The manuscript describes the various parts of this method for localization, source separation, confined heat elevation, triggering of cell death, and monitoring the response to treatment through fluorescence signaling. The entire system continues to evolve into a minimally invasive trans-endoscopic set-up. This article is categorized under: Diagnostic Tools > In Vivo Nanodiagnostics and Imaging Therapeutic Approaches and Drug Discovery > Nanomedicine for Oncologic Disease.
Keywords: fluorescence; magneto-acoustics; nano-particles; theranostic; thermal imaging.
© 2022 The Author. WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures







References
-
- Anderson, R. , & Parrish, J. (1981). The optics of human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 77(1), 13–19. - PubMed
-
- Andrä W, Nowak H. (2007) Magnetism in medicine: A handbook. Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. 10.1002/9783527610174 - DOI
-
- Becker, W. (2019). The Bh TCSPC handbook (8th ed.). Becker and Hickl. http://www.becker-hickl.de/handbook.htm
-
- Cohen, R., Lide, D., & Trigg, G. (2003). AIP Physics Desk Reference. Springer.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

