Heat shock factor 2-binding protein promotes tumor progression via activation of MAPK signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35435115
- PMCID: PMC9161939
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2063561
Heat shock factor 2-binding protein promotes tumor progression via activation of MAPK signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
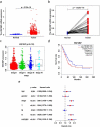
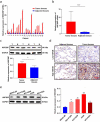
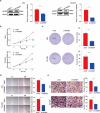
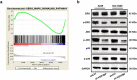
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a malignant tumor that causes a serious public health burden. The biological functions and potential mechanism of heat shock factor 2-binding protein (HSF2BP) in LUAD have not been studied. This study aimed to explore the HSF2BP expression pattern and its potential biological function in LUAD. The transcriptome data and relevant clinical data of LUAD were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The mRNA levels and prognosis of HSF2BP were determined using TCGA datasets. The protein and mRNA expression levels of HSF2BP were identified by conducting western blot analysis and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in tissues and cells, respectively. To determine whether HSF2BP affected the biological function of LUAD cell lines, a series of functional experiments were performed in vitro and in vivo. In addition, gene set enrichment analysis was applied to determine the pathways that HSF2BP regulated, which was further confirmed by western blotting, and the high expression of HSF2BP was observed in LUAD, which was correlated with the unfavorable prognosis in LUAD patients. Clinical correlation analysis revealed that tumor stage was positively correlated with high HSF2BP expression. Furthermore, HSF2BP could serve as an independent risk factor for overall survival. In vitro, HSF2BP knockdown suppressed the proliferation and migration of A549 and H1299 cells. We observed the same results in vivo experiments. Mechanistically, the HSF2BP regulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway to perform its biological function. The HSF2BP plays a role in the development of LUAD and could be a useful anticancer target for the treatment of LUAD.
Keywords: HSF2BP; MAPK signaling pathway; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. [published Online First: 2021/02/05]. - PubMed
-
- Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR.. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(8):1623–1640. [published Online First: 2019/08/06]. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer,version 5.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017;15(4):504–535. [published Online First: 2017/04/14]. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–454. [published Online First: 2018/01/25]. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rabe KF. Precision diagnosis and treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(9):849–861. [published Online First: 2017/08/31]. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
