Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with enhanced procoagulant activity in liver cirrhosis patients with portal vein thrombosis
- PMID: 35435260
- PMCID: PMC9102620
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24433
Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with enhanced procoagulant activity in liver cirrhosis patients with portal vein thrombosis
Abstract
Objective: Patients with liver cirrhosis (LC) commonly exhibit hypercoagulability and tend to develop thrombosis. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are associated with a variety of thrombotic conditions, but their possible value in portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is not known. We assessed whether NETs promote thrombosis and contribute to the procoagulant state in patients with LC.
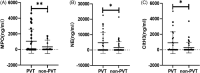
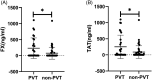
Methods: The circulating levels of NETs markers (myeloperoxidase, neutrophil elastase, citrullinated histone H3) were measured in 72 patients (median age, 55 years; 48 [66.7%] men) with LC from September 2020 to February 2021. Then they were divided into two groups: patients with or without PVT. NETs procoagulant activity was assessed based on thrombin-antithrombin complex (TAT complex) and Factor X. The levels of plasma markers were determined by ELISA.
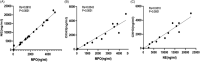
Results: There were 28 patients with PVT and 44 patients without PVT. The levels of NETs markers and hypercoagulability markers in the plasma of cirrhosis patients with PVT were significantly higher than those of cirrhosis patients without PVT (p < 0.05). Additionally, the levels of the NETs markers correlated with TAT complex and Factor X (Spearman correlation rho >0.73, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Neutrophil extracellular traps seem to enhance procoagulant activity in LC patients with PVT; thus, they may be a practical predictor of PVT as well as a rapid and easy-to-use diagnostic and treatment guide for PVT in patients with cirrhosis.
Keywords: hypercoagulability; liver cirrhosis; neutrophil extracellular traps; portal vein thrombosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors had conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GSDMD-Dependent Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Mediate Portal Vein Thrombosis and Associated Fibrosis in Cirrhosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9099. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169099. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201786 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps formation may be involved in the association of propranolol with the development of portal vein thrombosis.Thromb Res. 2024 Jun;238:208-221. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2024.04.030. Epub 2024 May 1. Thromb Res. 2024. PMID: 38733693
-
Contact System Activation and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Markers: Risk Factors for Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019 Jan-Dec;25:1076029618825310. doi: 10.1177/1076029618825310. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019. PMID: 30808222 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal vein thrombosis.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021 Oct;27(4):535-552. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0109. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34130370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of portal system hemodynamics for the prediction of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis-A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Ultrasound. 2023 Sep;51(7):1248-1258. doi: 10.1002/jcu.23523. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Clin Ultrasound. 2023. PMID: 37459439
Cited by
-
The implication of neutrophil extracellular traps in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 2;14:1292679. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1292679. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum proteomic profiling of patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease with and without clinically significant portal hypertension.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 11;19(4):e0301416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301416. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38603681 Free PMC article.
-
The Imbalance of Homeostasis in Neutrophil Extracellular Traps is Associated with Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024 Dec 28;12(12):1009-1019. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00165. Epub 2024 Nov 4. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39649033 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of neutrophil extracellular traps biomarkers in thrombosis.Thromb J. 2022 Oct 12;20(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12959-022-00421-y. Thromb J. 2022. PMID: 36224604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of neutrophil extracellular traps in venous thrombosis.Thromb J. 2023 Jun 16;21(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12959-023-00512-4. Thromb J. 2023. PMID: 37328882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

