The first detection of quaternary ammonium compounds in breast milk: Implications for early-life exposure
- PMID: 35437305
- PMCID: PMC9015285
- DOI: 10.1038/s41370-022-00439-4
The first detection of quaternary ammonium compounds in breast milk: Implications for early-life exposure
Abstract
Background: Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs), commonly used in cleaning, disinfecting, and personal care products, have recently gained worldwide attention due to the massive use of disinfectants during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, despite extensive use of these chemicals, no studies have focused on the analysis of QACs in human milk, a major route of exposure for infants.
Objective: Our objectives were to identify and measure QACs in breast milk and evaluate early-life exposure to this group of compounds for nursing infants.
Methods: Eighteen QACs, including 6 benzylalkyldimethyl ammonium compounds (BACs, with alkyl chain lengths of C8-C18), 6 dialkyldimethyl ammonium compounds (DDACs, C8-C18), and 6 alkyltrimethyl ammonium compounds (ATMACs, C8-C18), were measured in breast milk samples collected from U.S. mothers. Daily lactational intake was estimated based on the determined concentrations for 0-12 month old nursing infants.
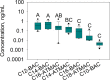
Results: Thirteen of the 18 QACs were detected in breast milk and 7 of them were found in more than half of the samples. The total QAC concentrations (ΣQAC) ranged from 0.33 to 7.4 ng/mL (median 1.5 ng/mL). The most abundant QAC was C14-BAC with a median concentration of 0.45 ng/mL. The highest median ΣQAC estimated daily intake (EDI) was determined for <1-month old infants based on the average (using the median concentration) and high (using the 95th percentile concentration) exposure scenarios (230 and 750 ng/kg body weight/day, respectively).
Significance: Our findings provide the first evidence of the detection of several QACs in breast milk and identify breastfeeding as an exposure pathway to QACs for nursing infants.
Impact statement: Our findings provide the first evidence of QAC occurrence in breast milk and identify breastfeeding as one of the exposure pathways to QACs for nursing infants.
Keywords: Biomonitoring; Child Exposure/Health; Early-life Exposure; Emerging Contaminants.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Surface disinfectant market size to reach USD 1,547.7 million by 2027; Rising prevalence of hospital-acquired infections to boost growth, Fortune Business Insights, June, 2020.
-
- Mulder I, Siemens J, Sentek V, Amelung W, Smalla K, Jechalke S. Quaternary ammonium compounds in soil: Implications for antibiotic resistance development. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2017;17:159–85. doi: 10.1007/s11157-017-9457-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

