Analysis of Systolic Blood Pressure Level and Short-Term Variability in Masked Hypertension
- PMID: 35437462
- PMCID: PMC9013288
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8016893
Analysis of Systolic Blood Pressure Level and Short-Term Variability in Masked Hypertension
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Analysis of Systolic Blood Pressure Level and Short-Term Variability in Masked Hypertension.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 16;2023:9761938. doi: 10.1155/2023/9761938. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37621630 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Patients with masked hypertension are at an elevated risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause death. This risk is close to that of sustained hypertension. The mean value and short-term variability of systolic blood pressure are considered to be risk factors for organ damage in hypertension.
Objective: To investigate the mean value and short-term variability of systolic blood pressure in patients with masked hypertension.
Methods: According to the results of in-clinic and ambulatory blood pressure measurement, participants were divided into four groups: normotension group, controlled hypertension group, masked hypertension group, and sustained hypertension group. The mean value and short-term variability of systolic blood pressure of masked hypertension group were evaluated by comparison with the other three groups.
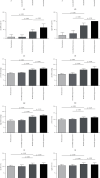
Results: A total of 250 subjects were enrolled, with an average age of 65.46 ± 8.76 years, and 166 (66.4%) were male, including 62 in the normotension group, 78 in the controlled hypertension group, 69 in the masked hypertension group, and 41 in the sustained hypertension group. Compared with the normotension group and controlled hypertension group, the mean value, blood pressure load, standard deviation, and coefficient of variation of systolic blood pressure over 24 hours and during the day and night, were all higher in the masked hypertension group (P < 0.05), while the rate of the nocturnal systolic blood pressure decline was lower (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the above indexes between the masked hypertension group and sustained hypertension group (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: There are higher mean value of systolic blood pressure and greater short-term variability in masked hypertension patients. Identification of masked hypertension is an important challenge in the clinic.
Copyright © 2022 Yinjing Hou and Bo Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-term variability and nocturnal decline in ambulatory blood pressure in normotension, white-coat hypertension, masked hypertension and sustained hypertension: a population-based study of older individuals in Spain.Hypertens Res. 2017 Jun;40(6):613-619. doi: 10.1038/hr.2017.9. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Hypertens Res. 2017. PMID: 28179625
-
Blood pressure variability in elderly persons with white-coat and masked hypertension compared to those with normotension and sustained hypertension.Am J Hypertens. 2013 Mar;26(3):367-72. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hps054. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Am J Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23382487
-
Strategies for classifying patients based on office, home, and ambulatory blood pressure measurement.Hypertension. 2015 Jun;65(6):1258-65. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.05038. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25870194
-
Controversies in Hypertension I: The Optimal Assessment of Blood Pressure Load and Implications for Treatment.Am J Med. 2022 Sep;135(9):1043-1050. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.05.007. Epub 2022 May 28. Am J Med. 2022. PMID: 35636476 Review.
-
Task force IV: Clinical use of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Participants of the 1999 Consensus Conference on Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring.Blood Press Monit. 1999 Dec;4(6):319-31. doi: 10.1097/00126097-199912000-00005. Blood Press Monit. 1999. PMID: 10602536 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Analysis of Systolic Blood Pressure Level and Short-Term Variability in Masked Hypertension.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 16;2023:9761938. doi: 10.1155/2023/9761938. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37621630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang D.-Y., Guo Q.-H., An D.-W., Li Y., Wang J.-G. A comparative meta-analysis of prospective observational studies on masked hypertension and masked uncontrolled hypertension defined by ambulatory and home blood pressure. Journal of Hypertension . 2019;37(9):1775–1785. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002109. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

