Imaging Features of Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease: Consensus Definitions From an International Multidisciplinary Working Group
- PMID: 35439343
- PMCID: PMC9579212
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.24898
Imaging Features of Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease: Consensus Definitions From an International Multidisciplinary Working Group
Abstract
Objective: To develop definitions for imaging features being considered as potential classification criteria for calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease, additional to clinical and laboratory criteria, and to compile example images of CPPD on different imaging modalities.
Methods: The American College of Rheumatology and European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology CPPD classification criteria Imaging Advisory Group (IAG) and Steering Committee drafted definitions of imaging features that are characteristic of CPPD on conventional radiography (CR), conventional computed tomography (CT), dual-energy CT (DECT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An anonymous expert survey was undertaken by a 35-member Combined Expert Committee, including all IAG members. The IAG and 5 external musculoskeletal radiologists with expertise in CPPD convened virtually to further refine item definitions and voted on example images illustrating CR, CT, and DECT item definitions, with ≥90% agreement required to deem them acceptable.
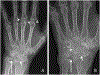
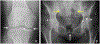
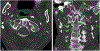
Results: The Combined Expert Committee survey indicated consensus on all CR definitions. The IAG and external radiologists reached consensus on CT and DECT item definitions, which specify that calcium pyrophosphate deposits appear less dense than cortical bone. The group developed an MRI definition and acknowledged limitations of this modality for CPPD. Ten example images for CPPD were voted acceptable (4 CR, 4 CT, and 2 DECT), and 3 images of basic calcium phosphate deposition were voted acceptable to serve as contrast against imaging features of CPPD.
Conclusion: An international group of rheumatologists and musculoskeletal radiologists defined imaging features characteristic of CPPD on CR, CT, and DECT and assembled a set of example images as a reference for future clinical research studies.
© 2022 American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
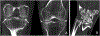
References
-
- Zhang W, Doherty M, Bardin T, et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I: terminology and diagnosis. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:563–70. - PubMed
-
- Ramonda R, Musacchio E, Perissinotto E, et al. Prevalence of chondrocalcinosis in Italian subjects from northeastern Italy. The ProVA Study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009;27:981–84. - PubMed
-
- Maravic M, Ea HK. Hospital burden of gout, pseudogout and other crystal arthropathies in France. Joint Bone Spine 2015;82:326–9. - PubMed
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Naimark A, Kannel W, Meenan RF. The prevalence of chondrocalcinosis in the elderly and its association with knee osteoarthritis: the Framingham Study. J Rheumatol 1989;16:1241–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

